Silk microneedles deliver controlled-release drugs painlessly

The tiny needles can be fabricated under normal temperature and pressure and from water, so they can be loaded with sensitive biochemical compounds and maintain their activity prior to use. They are also biodegradable and biocompatible.
The research paper “Fabrication of Silk Microneedles for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery” appeared in Advanced Functional Materials December 2 online in advance of print.
The Tufts researchers successfully demonstrated the ability of the silk microneedles to deliver a large-molecule, enzymatic model drug, horseradish peroxidase (HRP), at controlled rates while maintaining bioactivity. In addition, silk microneedles loaded with tetracycline were found to inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, demonstrating the potential of the microneedles to prevent local infections while also delivering therapeutics.
“By adjusting the post-processing conditions of the silk protein and varying the drying time of the silk protein, we were able to precisely control the drug release rates in laboratory experiments,” said Fiorenzo Omenetto, Ph.D., senior author on the paper. “The new system addresses long-standing drug delivery challenges, and we believe that the technology could also be applied to other biological storage applications.”
The Drug Delivery Dilemma
While some drugs can be swallowed, others can't survive the gastrointestinal tract. Hypodermic injections can be painful and don't allow a slow release of medication. Only a limited number of small-molecule drugs can be transmitted through transdermal patches. Microneedles—no more than a micron in size and able to penetrate the upper layer of the skin without reaching nerves—are emerging as a painless new drug delivery mechanism. But their development has been limited by constraints ranging from harsh manufacturing requirements that destroy sensitive biochemicals, to the inability to precisely control drug release or deliver sufficient drug volume, to problems with infections due to the small skin punctures.
The process developed by the Tufts bioengineers addresses all of these limitations. The process involves ambient pressure and temperature and aqueous processing. Aluminum microneedle molding masters were fabricated into needle arrays of about 500 µm needle height and tip radii of less than 10 µm. The elastomer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) was cast over the master to create a negative mold; a drug-loaded silk protein solution was then cast over the mold. When the silk was dry, the drug-impregnated silk microneedles were removed. Further processing through water vapor annealing and various temperature, mechanical and electronic exposures provided control over the diffusity of the silk microneedles and drug release kinetics.
“Changing the structure of the secondary silk protein enables us to 'pre-program' the properties of the microneedles with great precision,” said David L. Kaplan, Ph.D., coauthor of the study, chair of biomedical engineering at Tufts and a leading researcher on silk and other novel biomaterials. “This is a very flexible technology that can be scaled up or down, shipped and stored without refrigeration and administered as easily as a patch or bandage. We believe the potential is enormous.”
Other co-authors on the paper, all associated with the Department of Biomedical Engineering, are Konstantinos Tsioris, doctoral student; Waseem Raja, post-doctoral associate; Eleanor Pritchard, post-doctoral associate; and Bruce Panilaitis, research assistant professor.
The research was based on work supported in part by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory, the U.S. Army Research Office, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency-Defense Sciences Office and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
Tsioris, K., Raja, W. K., Pritchard, E. M., Panilaitis, B., Kaplan, D. L. and Omenetto, F. G. (2011), Fabrication of Silk Microneedles for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery. Advanced Functional Materials. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201102012
Located on Tufts' Medford/Somerville campus, the School of Engineering offers a rigorous engineering education in a unique environment that blends the intellectual and technological resources of a world-class research university with the strengths of a top-ranked liberal arts college. Close partnerships with Tufts' undergraduate, graduate and professional schools, coupled with a long tradition of collaboration, provide a strong platform for interdisciplinary education and scholarship. The School of Engineering's mission is to educate engineers committed to the innovative and ethical application of science and technology in addressing the most pressing societal needs, to develop and nurture twenty-first century leadership qualities in its students, faculty, and alumni, and to create and disseminate transformational new knowledge and technologies that further the well-being and sustainability of society in such cross-cutting areas as human health, environmental sustainability, alternative energy, and the human-technology interface.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.tufts.eduAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles
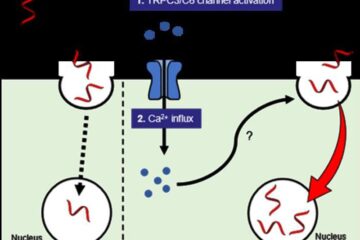
Next-generation treatments hitch a ride into cancer cells
Researchers from Osaka University discover that opening a channel into cancer cells helps antisense oligonucleotide drugs reach their targets. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are next-generation drugs that can treat disease by…

Boron deficiency: oilseed rape reacts as with infection and pest infestation
Genetic mechanisms uncovered… Boron deficiency has a devastating effect on oilseed rape and related plants. However, little is known about the underlying genetic mechanisms. A study shows that the response…
Quantum Precision: A New Kind of Resistor
Researchers at the University of Würzburg have developed a method that can improve the performance of quantum resistance standards. It´s based on a quantum phenomenon called Quantum Anomalous Hall effect….