Carbon nanotubes eliminate manufacturing woe
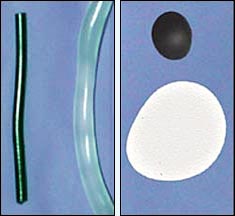
Two examples of how nanotube-filled polymers (thin rod in left photo; small disk in right photo) avoid swelling seen in traditional polymers.
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have discovered that the addition of carbon nanotubes to a common commercial polymer, polypropylene, leads to dramatic changes in how the molten polymer flows. This process eliminates a widespread manufacturing headache known as “die-swell” in which polymers swell in undesirable directions when passing through the exit port of an extruder (a machine for producing more or less continuous lengths of plastic sections).
Researchers have been adding small amounts of nanotubes–tiny tubes of carbon about 1,000 times thinner than a human hair–to polypropylene in hopes of dramatically enhancing the material’s strength and other properties. Once realized, this enhanced polymer could be processed at high speed through extruders for use in manufacturing.
NIST materials scientists were concerned that because nanotubes make the polypropylene rubbery, the material would be difficult to process or its enhanced properties would be lost. To their surprise, the opposite proved true. When sheared (forced) between two plates, the polymer normally separates the plates. However, when nanotubes are added, the plates are pulled together.
The scientists discovered that this “pulling-together” completely alleviated die-swell. Industry currently uses various time-consuming trial-and-error solutions to deal with the problem. Eliminating die-swell should help manufacturers improve their time-to-market by simplifying their die design processes and enabling the controlled manufacture of smaller components.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nist.govAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…