Nanotube fibers in a jiffy
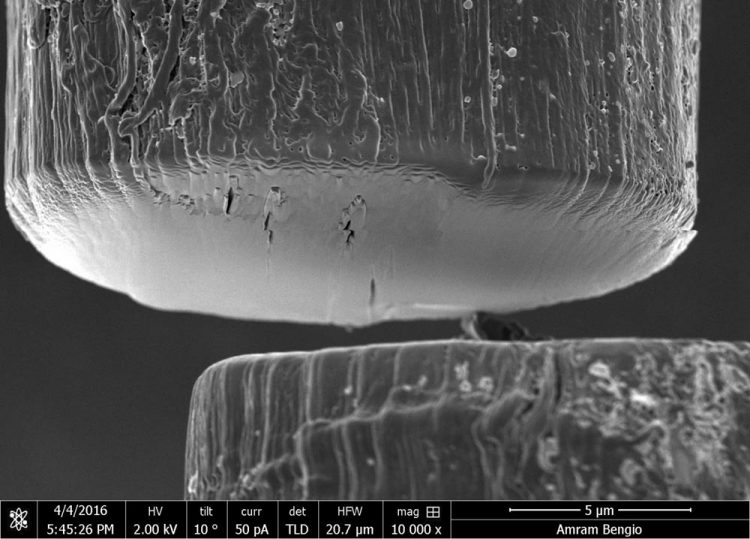
Thread-like fibers created with a new, rapid method at Rice University are made of billions of carbon nanotubes that can be quickly aligned by shear force between slides. Credit: Complex Forms of Complex Fluids/Rice University
The terms “handmade” and “high tech” are not commonly found in the same sentence, but they both apply to a Rice University method to quickly produce fibers from carbon nanotubes.
The method developed by the Rice lab of chemist Matteo Pasquali allows researchers to make short lengths of strong, conductive fibers from small samples of bulk nanotubes in about an hour.
The work complements Pasquali's pioneering 2013 method to spin full spools of thread-like nanotube fibers for aerospace, automotive, medical and smart-clothing applications. The fibers look like cotton thread but perform like metal wires and carbon fibers.
It can take grams of material and weeks of effort to optimize the process of spinning continuous fibers, but the new method cuts that down to size, even if it does require a bit of hands-on processing.
Pasquali and lead author and graduate student Robby Headrick reported in Advanced Materials that aligning and twisting the hair-like fibers is fairly simple.
First, Headrick makes films. After dissolving a small amount of nanotubes in acid, he places the solution between two glass slides. Moving them quickly past each other applies shear force that prompts the billions of nanotubes within the solution to line up. Once the resulting films are deposited onto the glass, he peels off sections and rolls them up into fibers.
“The film is in a gel state when I peel it, which is important to get a fully densified fiber,” Headrick said. “You twist it when it's wet throughout the cross section of the structure, and when you dry it, the capillary pressure densifies it.”
Headrick was dissatisfied with the reproducibility of his initial experiments and discussed the procedure with his father, Robert, an amateur woodworker. The elder Headrick quickly came up with a simple device to support the slides and control the shearing process.
The dried nanotube fibers are about 7 centimeters long; the electrical performance is equivalent to long fibers created by the original spinning method but even more dense with a tensile strength up to 3.5 gigapascals (GPa), better than spun fibers. The researchers expect that nanotubes 50,000 to 70,000 times longer than they are wide will produce fibers of 35 to 40 GPa, about the strength of an individual carbon nanotube.
“We can process all kinds of nanotubes the exact same way so we get optimal fiber structures and properties,” Headrick said. “It speeds things up and allows us to explore nanotubes that are only available in small quantities.”
Pasquali said the process reproduces the high nanotube alignment and high packing density typical of fibers produced via spinning, but at a size sufficient for strength and conductivity tests.
“We now use this as a quick lab test to assess new materials and to create target properties for the large-scale method,” Pasquali said. “We'll know in advance what the material can deliver, whereas before, we could only infer it. This could be especially important for carbon nanotube producers who want to change their reactor conditions to give them quick feedback or for quality control, as well as for testing samples that have been sorted by metallic versus semiconductor type or even helicity.”
###
Co-authors of the paper are Rice alumni Dmitri Tsentalovich, now of DexMat Inc., and Julián Berdegué and graduate student Amram Bengio; Matthew Lucas of the Universal Technology Corp. and Air Force Research Laboratory, Dayton, Ohio; and students Lucy Liberman and Olga Kleinerman and Yeshayahu Talmon, a professor emeritus of chemical engineering, of Technion-Israel Institute of Technology. Pasquali is a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, of materials science and nanoengineering and of chemistry, and chair of Rice's Department of Chemistry.
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the United States-Israel Binational Science Foundation and a NASA Space Technology Research Fellowship supported the research.
Read the abstract at http://onlinelibrary.
This news release can be found online at http://news.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
Video:
Video produced by Brandon Martin/Rice University
Related materials:
Complex Forms of Complex Fluids (Pasquali group): https:/
Talmon Group: http://talmon.
Wiess School of Natural Sciences: http://natsci.
Images for download:
http://news.
Rice University scientists have created a method to quickly align carbon nanotubes on a slide, seen here under a microscope. The films can be peeled and twisted by hand into short carbon nanotube fibers for testing. (Credit: Complex Forms of Complex Fluids/Rice University)
http://news.
Thread-like fibers created with a new, rapid method at Rice University are made of billions of carbon nanotubes that can be quickly aligned by shear force between slides. (Credit: Complex Forms of Complex Fluids/Rice University)
http://news.
Robby Headrick uses a device built by his father, a woodworker, that holds one slide stable while the other is moved to create shear forces that align carbon nanotubes between them. The nanotubes form a film that can be peeled and rolled by hand to create short nanofibers for testing. (Credit: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
http://news.
Rice University graduate student Robby Headrick peels a strip of aligned carbon nanotubes from a slide. The lab's method for making short nanotubes takes weeks off the time needed to make samples for testing. (Credit: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
http://news.
Robby Headrick rolls a strip of aligned nanotubes into a nanofiber in a Rice University laboratory. (Credit: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
http://news.
Matteo Pasquali, left, and Robby Headrick. (Credit: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction and No. 2 for happiest students by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read “What they're saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.
David Ruth
713-348-6327
david@rice.edu
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
mikewilliams@rice.edu
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…