Electronics: Graphene sheets’ growing attractions
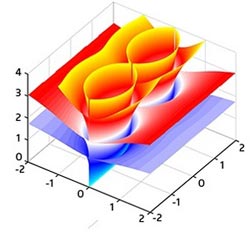
Plasmon energy states in an array of four graphene sheets. Each plane represents different plasmon energy states resulting from different numbers of electrons in each sheet. <br><br><br><br>Copyright : 2012 A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering<br>
One-atom-thick sheets of carbon — known as graphene — have a range of electronic properties that scientists are investigating for potential use in novel devices.
Graphene’s optical properties are also garnering attention, which may increase further as a result of research from the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE). Bing Wang of the IMRE and his co-workers have demonstrated that the interactions of single graphene sheets in certain arrays allow efficient control of light at the nanoscale1.
Light squeezed between single graphene sheets can propagate more efficiently than along a single sheet. Wang notes this could have important applications in optical-nanofocusing and in superlens imaging of nanoscale objects.
In conventional optical instruments, light can be controlled only by structures that are about the same scale as its wavelength, which for optical light is much greater than the thickness of graphene. By utilizing surface plasmons, which are collective movements of electrons at the surface of electrical conductors such as graphene, scientists can focus light to the size of only a few nanometers.
Wang and his co-workers calculated the theoretical propagation of surface plasmons in structures consisting of single-atomic sheets of graphene, separated by an insulating material. For small separations of around 20 nanometers, they found that the surface plasmons in the graphene sheets interacted such that they became ‘coupled’ (see image). This theoretical coupling was very strong, unlike that found in other materials, and greatly influenced the propagation of light between the graphene sheets.
The researchers found, for instance, that optical losses were reduced, so light could propagate for longer distances. In addition, under a particular incoming angle for the light, the study predicted that the refraction of the incoming beam would go in the direction opposite to what is normally observed. Such an unusual negative refraction can lead to remarkable effects such as superlensing, which allows imaging with almost limitless resolution.
As graphene is a semiconductor and not a metal, it offers many more possibilities than most other plasmonic devices, comments the IMRE’s Jing Hua Teng, who led the research. “These graphene sheet arrays may lead to dynamically controllable devices, thanks to the easier tuning of graphene’s properties through external stimuli such as electrical voltages.” Graphene also allows for an efficient coupling of the plasmons to other objects nearby, such as molecules that are adsorbed on its surface. Teng therefore says that the next step is to further explore the interesting physics in graphene array structures and look into their immediate applications.
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering
Journal information
Wang, B., Zhang, X., García-Vidal, F. J., Yuan, X. & Teng, J. Strong coupling of surface plasmon polaritons in monolayer graphene sheet arrays. Physical Review Letters 109, 073901 (2012).
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















