Computer simulations reveal universal increase in electrical conductivity
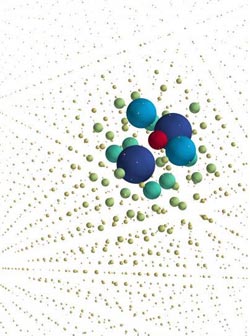
This image shows simulated correlation function for thermally excited charge pairs in a strong electric field. The lattice simulations provide access to atomic-scale details, giving new insights into the universal increase of electric conductivity predicted by Onsager in 1934.<br><br>Credit: Credit: London Centre for Nanotechnology<br>
The study, published in Nature Materials, investigated the electrical conductivity of a solid electrolyte, a system of positive and negative atoms on a crystal lattice. The behaviour of this system is an indicator of the universal behaviour occurring within a broad range of materials from pure water to conducting glasses and biological molecules.
Electrical conductivity, a measure of how strongly a given material conducts the flow of electric current, is generally understood in terms of Ohm's law, which states that the conductivity is independent of the magnitude of an applied electric field, i.e. the voltage per metre.
This law is widely obeyed in weak applied fields, which means that most material samples can be ascribed a definite electrical resistance, measured in Ohms.
However, at strong electric fields, many materials show a departure from Ohm's law, whereby the conductivity increases rapidly with increasing field. The reason for this is that new current-carrying charges within the material are liberated by the electric field, thus increasing the conductivity.
Remarkably, for a large class of materials, the form of the conductivity increase is universal – it doesn't depend on the material involved, but instead is the same for a wide range of dissimilar materials.
The universality was first comprehended in 1934 by the future Nobel Laureate Lars Onsager, who derived a theory for the conductivity increase in electrolytes like acetic acid, where it is called the “second Wien effect”. Onsager's theory has recently been applied to a wide variety of systems, including biochemical conductors, glasses, ion-exchange membranes, semiconductors, solar cell materials and to “magnetic monopoles” in spin ice.
Researchers at the London Centre for Nanotechnology (LCN), the Max Plank Institute for Complex Systems in Dresden, Germany and the University of Lyon, France, succeeded for the first time in using computer simulations to look at the second Wien effect. The study, by Vojtech Kaiser, Steve Bramwell, Peter Holdsworth and Roderich Moessner, reveals new details of the universal effect that will help interpret a wide varierty of experiments.
Professor Steve Bramwell of the LCN said: “Onsager's Wien effect is of practical importance and contains beautiful physics: with computer simulations we can finally explore and expose its secrets at the atomic scale.
“As modern science and technology increasingly explores high electric fields, the new details of high field conduction revealed by these simulations, will have increasing importance.”
Notes to editors
For more information, contact David Weston in the UCL Press Office on +44 (0) 203 108 3844 (out of hours 07917 271 364) or d.weston@ucl.ac.uk
Journal link: 'Onsager's Wien effect on a lattice', Nature Materials Advance Online Publication, 11th August 2013; DOI: 10.1038/NMAT3729
Image caption: Simulated correlation function for thermally excited charge pairs in a strong electric field. The lattice simulations provide access to atomic-scale details, giving new insights into the universal increase of electric conductivity predicted by Onsager in 1934.
About UCL (University College London)
Founded in 1826, UCL was the first English university established after Oxford and Cambridge, the first to admit students regardless of race, class, religion or gender and the first to provide systematic teaching of law, architecture and medicine. We are among the world's top universities, as reflected by our performance in a range of international rankings and tables. According to the Thomson Scientific Citation Index, UCL is the second most highly cited European university and the 15th most highly cited in the world. UCL has nearly 27,000 students from 150 countries and more than 9,000 employees, of whom one third are from outside the UK. The university is based in Bloomsbury in the heart of London, but also has two international campuses – UCL Australia and UCL Qatar. Our annual income is more than £800 million.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ucl.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
In a significant milestone for quantum communication technology, an experiment has demonstrated how networks can be leveraged to combat disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communications. The international effort led by researchers…

Stretchable quantum dot display
Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes achieved record-breaking performance. A team of South Korean scientists led by Professor KIM Dae-Hyeong of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for…

Internet can achieve quantum speed with light saved as sound
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute have developed a new way to create quantum memory: A small drum can store data sent with light in its sonic…





















