A new form of hybrid photodetectors with quantum dots and graphene
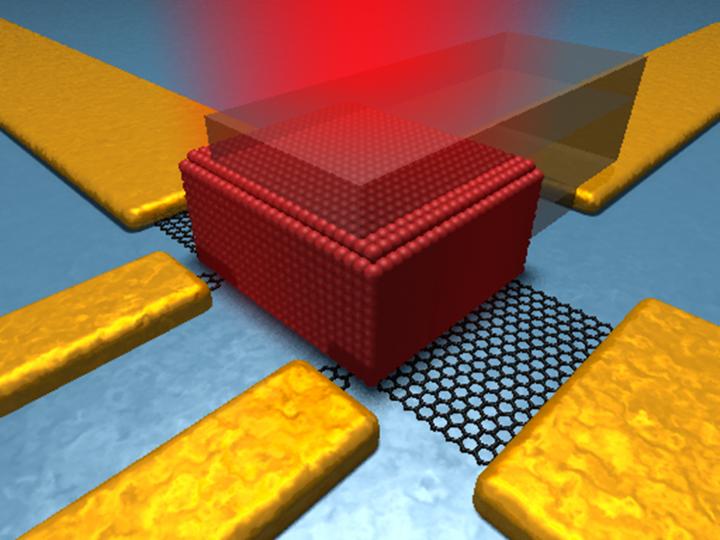
This is a schematic of the device structure. Credit: ICFO
Many efforts have been focused towards optoelectronic research in trying to create low cost photodetectors with high sensitivity, high quantum efficiency, high gain and fast photoresponse. This is of paramount importance especially in the short wave infrared which currently is addressed by very expensive III-V InGaAs photodetectors.
The development of two main classes of photodetectors, photodiodes and phototransistors, have partially been able to accomplish these goals because even though they both have many outstanding properties, none seem to fulfill all of these requirements. While photodiodes are much faster than phototransistors, phototransistors have a higher gain and do not require low noise preamplifiers for their use.
To overcome these limitations, ICFO researchers Ivan Nikitskiy, Stijn Goossens, Dominik Kufer, Tania Lasanta, Gabriele Navickaite, led by ICREA professors at ICFO Frank Koppens and Gerasimos Konstantatos, have been able to develop a hybrid photodetector capable of attaining concomitantly better performance features in terms of speed, quantum efficiency and linear dynamic range, operating not only in the visible but also in the near infrared (NIR: 700-1400nm) and SWIR range (1400-3000nm).
At the same time this technology is based upon materials that can be monolithically integrated with Si CMOS electronics as well as flexible electronic platforms. The results of this work have been recently published in Nature Communications.
To be able to achieve this, the team of researchers developed a hybrid device by integrating an active colloidal quantum dot photodiode with a graphene phototransistor. By including an “active” quantum dot photodiode, they were able to increase charge collection in a highly absorbing thick QD film, which in turn increased the quantum efficiency as well as the photoresponse.
The active quantum dot layer enabled a more effective charge collection by exploiting carrier drift towards the graphene layer instead of relying only on diffusion. The researchers then combined this scheme with a graphene transistor to register ultra-high-gains and record gain-bandwidth products, thanks to Graphene's 2D character and remarkably high carrier mobility.
The results obtained in this study have shown that this hybrid architecture does clearly demonstrate the potential of graphene and active quantum dot materials, opening new pathways for their integration in other optoelectronic materials in search for much higher performance and a broader spectrum of functionalities.
###
Link to the paper: http://www.
Link to the research group led by ICREA Prof. at ICFO Gerasimos Konstantatos: https:/
Link to the research group led by ICREA Prof. at ICFO Frank Koppens: https:/
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















