Stretchable circuits: New process simplifies production of functional prototypes
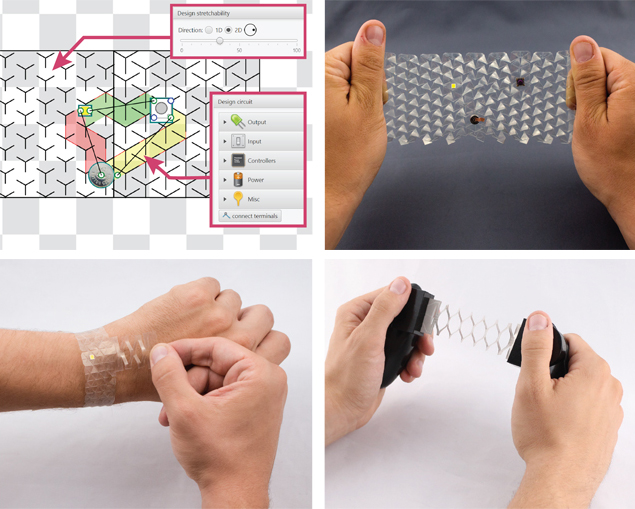
By applying their new approach the researchers produced three prototypes, each taking less than five minutes. Foto: Saar-Uni
A jacket that silences incoming calls when its sleeve is plucked. A bandage that sounds an alarm when the joint is bent too much. These are two of many applications that are only possible with stretchable circuits.
“However, current manufacturing processes are time-consuming and very complex,” explains Daniel Gröger, a doctoral student in computer science at Saarland University. Hence, together with Professor Jürgen Steimle, Gröger has developed a process to produce stretchable circuits within a few minutes. The heart of the process is a so-called laser cutter.
Its laser beam continuously removes targeted material. In this way, it makes many precise cuts in a very short time. The researchers take advantage of this by having the laser cut a certain pattern into the material, similar to a Y shape. The size of the pattern, the thickness of its lines and the distance between the cuts determine the elasticity of the material.
The material consists of a conductive and a non-conductive layer. The circuit is created by the laser ablating the conductive layer at pre-defined points during cutting.
Since it is not only fast, accurate cutting that difficult for humans, but also the planning of where to cut, the researchers have automated that, too. The result is software allowing designers to specify the outline of the piece, similar to a drawing program, and determine which part of it should be stretchable. They determine the degree of elasticity using a virtual slider. Finally, they place the electronic components.
The software then calculates the position and nature of the Y shapes, including the circuit diagram, and displays everything. The fast result is unusual, because the calculation of the best ladder route so far has required a lot of computing time and power. The researchers, however, have devised a shortcut by presenting the calculation problem as a graph, for which efficient calculation is possible.
In this way, the researchers produced three prototypes, each taking less than five minutes. The first is a transparent bracelet with a light-emitting diode. On its side is a tab, similar to the rotating wheel on the side of a watch. Pulling on either the strap or on the tab switches the light emitting diode on and off. This fulfills the basic functionality of a stopwatch, says Gröger. Pulling the strap corresponds to starting and stopping.
If you pull the wristband, the time measurement starts again. The other two prototypes are a flexible controller for computer games and a sensor that is integrated into an elbow bandage and measures the degree of diffraction. The materials used, such as plastic foils coated with indium tin oxide, are available online.
Gröger therefore believes that the new process also enables people who are not familiar with materials research to create stretchable circuits. The researchers point out that the current test models can withstand at least thousand strains, but this does not yet meet commercial quality criteria for durability. Nevertheless, Gröger is convinced: “Even if the technology still has to be improved, the concepts will hold”.
The scientists financed their research with funds from the Horizon 2020 program of the European Union and with funds from the Cluster of Excellence for Multimodal Computing and Interaction.
Press picture: www.uni-saarland.de/pressefotos
Editor:
Gordon Bolduan
Competence Center Computer Science Saarland
Saarland University
Saarland Informatics Campus E1.7
Phone: +49 681 302-70741
Email: bolduan@mmci.uni-saarland.de
Daniel Gröger
Human Computer Interaction
Saarland University
Saarland Informatics Campus E1.7
Phone: +49 681 302 71931
Email: groeger@cs.uni-saarland.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-saarland.deAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…