Optical fingerprint can reveal pollutants in the air
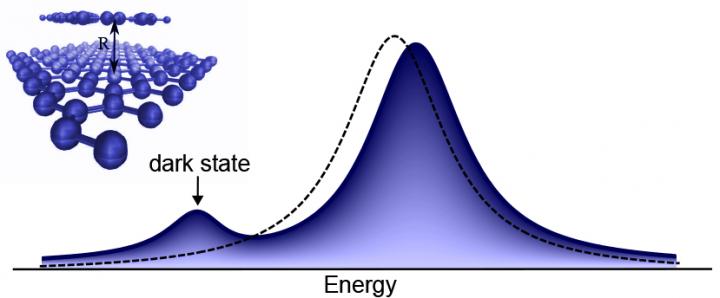
Molecules are identified by activating dark electronic states in the sensor material, resulting in a new visible peak. The altered optical fingerprint of the material proves the presence of molecules. Credit: Maja Feierabend and Ermin Malic
More efficient sensors are needed to be able to detect environmental pollution. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have proposed a new, sophisticated method of detecting molecules with sensors based on ultra-thin nanomaterials.
The novel method could improve environmental sensing in the future. The results are published today in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
“This could open up new possibilities for the detection of environmental gases. Our method is more robust than conventional sensors, which rely on small changes in optical properties”, says Maja Feierabend, PhD student at the Department of Physics and the main author of the article from Chalmers University of Technology and Technische Universität Berlin.
Together with her supervisor, Associate Professor Ermin Malic, and Gunnar Berghäuser, postdoctoral researcher at Chalmers, she has proposed a new type of chemical nanosensor that consists of atomically thin nanomaterials that are extremely sensitive to changes in their surroundings.
If you shine light on the sensor, you will see the optical fingerprint of the material itself. Molecules are identified by activating dark electronic states in the sensor material. If there are molecules on its surface, they will interact with these dark states and switch them on, making them visible. The result is an altered optical fingerprint, containing new features that prove the presence of the molecules.
“Our method has promising potential, paving the way for ultra-thin, fast, efficient and accurate sensors. In the future, this could hopefully lead to highly sensitive and selective sensors that can be used in environmental research”, says Ermin Malic.
The researchers have filed a patent application for the novel sensor method. The next step is to work with experimental physicists and chemists to demonstrate the proof-of-principle for this new class of chemical sensors.
###
Read the scientific article in Nature Communications: “Proposal for dark exciton based chemical sensors”
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















