Lipid nanodiscs stabilize misfolding protein intermediates red-handed
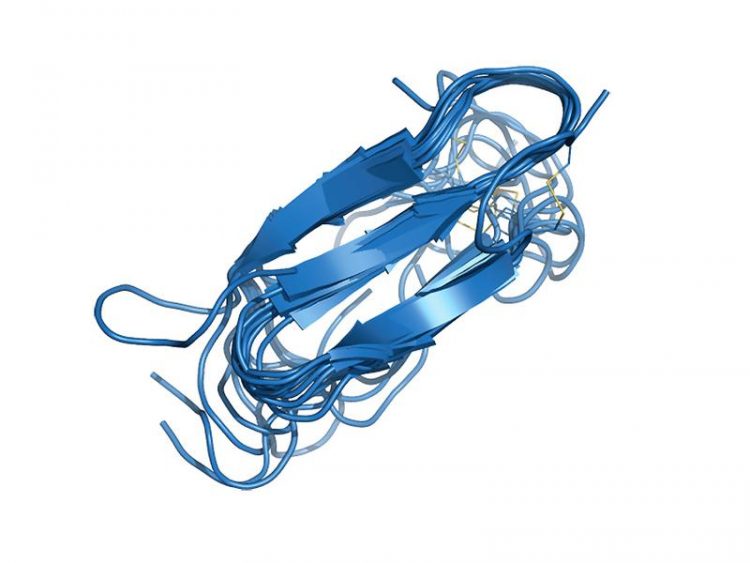
Superimposing the ten structures with the least energy shows nicely which structure the hIAPP molecule prefers in a membrane environment. Image: Diana Rodriguez Camargo / TUM
The clumps caused by misfolded proteins, called plaques, are implicated in many diseases: plaque interferes with neuron function in the brains of people with dementia and Alzheimer's. The process of the formation of plaques also kills islet cells, which produce insulin to metabolize sugar, in people with type 2 diabetes.
“In general, toxicity to cells is extremely difficult to prove and characterize,” said Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy, Professor at the University of Michigan and Hans Fischer Fellow of the Institute for Advanced Study at the Technical University of Munich. “On the other hand, we need to do this in order to develop drugs for potential treatment.”
Lipid nanodiscs stabilize aggregating proteins
To understand the critical protein structures, the researchers used “sushi-like” nanodics composed of layers of lipids surrounded by a belt to capture model proteins during the aggregation process.
The researchers allowed the proteins to fold to a certain point within the nanodisc – when they think the folding proteins are most toxic to islet cells – and then used nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to take atomic-level images of the proteins.
“The nanodiscs are like the difference between a swimming pool and the ocean. In the ocean, there are no boundaries; a swimming pool has boundaries,” Ramamoorthy said. “We're able to stop the aggregation of the protein in this restricted membrane environment so we can monitor what it looks like before it becomes a mass of fibers.”
A first step into development of drugs
The ability to pin down proteins while they’re in the process of amyloid aggregation in a stable manner allow their characterization using a variety of biophysical tools including fluorescence, mass-spectrometry, NMR, and cryo-electron-microscopy. Therewith the researchers hope to both develop and screen for drug compounds that can target the misfolding proteins that are implicated in these diseases.
“We are now screening interactions with small molecule compounds to see if we can inhibit the aggregation process that produces amyloids,” Ramamoorthy said. “This has been much wanted and much awaited information – for the scientific understanding of the pathology of amyloid diseases, and for the development of compounds to overcome these problems.”
The study was carried out by researchers at the Technical University of Munich, the University of Michigan, and the Helmholtz-Zentrum Muenchen in the framework of the TUM Institute of Advanced Study Focus Group “Protein Misfolding and Amyloid Diseases” where Prof. Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy worked as TUM-IAS Hans Fischer Senior Fellow hosted by Bernd Reif, Professor for Solid State NMR-Spectroscopy at TUM.
This work was supported by funds from NIH, the Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft and the German Research Foundation, the Cluster of Excellence „Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM) and the Institute for Advanced Study, funded by the German Excellence Initiative and the European Union Seventh Framework Program under grant agreement no. 291763. The Gauss Center for Supercomputing provided computing time at the Leibniz Supercomputing Center in Garching.
Publication:
Stabilization and structural analysis of a membrane-associated hIAPP aggregation intermediate
Diana C. Rodriguez Camargo, Kyle J. Korshavn, Alexander Jussupow, Kolio Raltchev, David Goricanec, Markus Fleisch, Riddhiman Sarkar, Kai Xue, Michaela Aichler, Gabriele Mettenleiter, Axel Karl Walch, Carlo Camilloni, Franz Hagn, Bernd Reif, Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy
eLife, 2017; 6:e31226 – DOI: 10.7554/eLife.31226
Link: https://elifesciences.org/articles/31226
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Bernd Reif
Technical University of Munich
Solid State NMR-Spectroscopy
Lichtenbergstr 4, 85747 Garching, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 289 52615 – e-mail: reif@tum.de – web: http://www.ocb.ch.tum.de
https://www.tum.de/nc/en/about-tum/news/press-releases/detail/article/34381/ Link to the press release
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















