Frigid Cloudtop Temperatures Indicate Strength in Super Typhoon Jelawat and Tropical Storm Ewinar
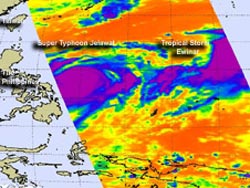
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite revealed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around the center of Typhoon Jelawat and a band of thunderstorms west of the center on Sept. 23.
Those thunderstorms continued to strengthen on Sept. 24 and cloud top temperatures exceeded -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius). Cloud top temperatures are an indication of uplift in a storm. Uplift is the push of air upward that allows formation of towering clouds and thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone.
Jelawat's center continues to stay east of the Philippines, but is causing rough surf (with wave heights up to 37 feet/11.2 meters) along the eastern coasts of the country and its large extent is bringing rains and gusty winds as well.
Jelawat is a powerful Super Typhoon with a clear 23 nautical mile-wide eye and maximum sustained winds near 130 knots (149.6 mph/240.8 kmh).Jelawat is a Category 4 typhoon on the Saffir-Simpson scale. It is located near 15.0 North latitude and 127.9 East longitude, approximately 410 nautical miles (472 miles/759 km) east of Manila, Philippines. Jelawat's minimum central pressure is near 926 millibars. Jelawat is forecast to track to the northwest through the Philippine Sea and move toward Taiwan.
Tropical Storm Ewinar had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/64.8 kmh) on Sept 24 at 1500 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT). It was centered near 20.9 North and 138.9 East, a 300 nautical miles (345 miles/555.6 km) south-southwest of Iwo To. AIRS data showed that the low-level center is slowly consolidating (organizing) and becoming less elongated. The strongest convection and thunderstorms were seen in a band of thunderstorms east of the center of circulation. Ewinar is getting organized slowly because of westerly wind shear caused by nearby Typhoon Jelawat.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects Ewinar to track to the north-northeast and affect Iwo Two tomorrow, Sept. 25 as it continues in a northeasterly direction.
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















