Crystal film growth: nanosheets extend epitaxial growth applications
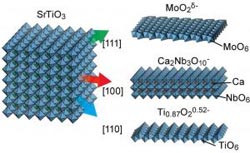
Schematic illustration of nanosheet structures for Ca2Nb3O10-, Ti0.87O20.52-, and MoO2ä− nanosheets and corresponding crystal planes of SrTiO3.<br>
Source: Research highlight from MANA, the International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics at NIMS, Tsukuba, Japan.
Tsukuba, Japan (MANA) 17 December 2013
MANA Research Highlights:
Epitaxial growth has become increasingly important for growing crystalline thin films with tailored electronic, optical and magnetic properties for technological applications. However the approach is limited by the high structural similarities required between an underlying substrate and a growing crystal layer on top of it.
Takayoshi Sasaki and colleagues at the International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (MANA) and the University of Tokyo in Japan demonstrate how using two-dimensional materials they can extend the versatility of epitaxial growth techniques.
In 1984 Komo proposed that certain layered materials such as mica or graphite can be easily cleaved to produce surfaces with no dangling bonds that would alleviate the lattice matching requirements for epitaxial growth.
Interactions between adatoms on these cleaved materials would be more prominent compared with growth on single crystalline substrates since the interlayer van der Waals interactions are weak. However the variety of suitable cleaved surfaces is limited and handling them can be difficult.
With the increasing attention on two-dimensional materials over recent years Takayoshi Sasaki and colleagues decided to look into molecularly thin two-dimensional crystals as possible seed layers to alleviate lattice matching requirements in a manner similar to Komo’s van der Waals epitaxy.
They deposited nanosheets of either Ca2Nb3O10-, Ti0.87O20.52-, or MoO2ä- as highly organised layers onto amorphous glass. On these different surfaces they grew different orientations of SrTiO3, an important perovskite for various technological applications. The approach demonstrated the ability to grow different orientations of SrTiO3 with a high level of precision.
The researchers suggest that in the future, it would be of great interest to achieve more sophisticated control of growth geometry using nanosheets with a complex structure. They add, “Such advanced design, hardly realized with present technology, will pave a new way for further development of crystal engineering.”
Contact Information
International Center of Materials Nanoarchitectonics (MANA)
National Institute for Materials Science
1-1 Namiki Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0044 JAPAN
Phone: +81-29-860-4710
E-mail: mana-pr@ml.nims.go.jp
About MANA
http;//www.nims.go.jp/mana/
MANA Research Highlights
Crystal film growth: nanosheets extend epitaxial growth applications
http://www.nims.go.jp/mana/research/highlight/vol8.html
Publisher
International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (WPI-MANA)
Address: 1-1 Namiki, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0044, Japan
URL: http://www.nims.go.jp/mana/
Journal information
Versatile van der Waals epitaxy-like growth of crystal films using two-dimensional nanosheets as a seed layer: Orientation tuning of SrTiO3 films along three important crystallographic axes of (100), (110) and (111) on glass substrate Tatsuo Shibata1, Hikaru Takano1, Yasuo Ebina1, Dae Sung Kim1, Tadashi C. Ozawa1, Kosho Akatsuka1,Tsuyoshi Ohnishi1, Kazunori Takada1, Toshihiro Kogure2, and Takayoshi Sasaki*1,2013 J. Mater. Chem. C DOI:10.1039/C3TC31787K
Affiliations
1. International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics, National Institute for Materials Science, 1-1 Namiki, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0044, Japan
2. Department of Earth and Planetary Science, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan
*Corresponding author.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
In a significant milestone for quantum communication technology, an experiment has demonstrated how networks can be leveraged to combat disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communications. The international effort led by researchers…

Stretchable quantum dot display
Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes achieved record-breaking performance. A team of South Korean scientists led by Professor KIM Dae-Hyeong of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for…

Internet can achieve quantum speed with light saved as sound
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute have developed a new way to create quantum memory: A small drum can store data sent with light in its sonic…





















