Salmonella use intestinal epithelial cells to colonize the gut
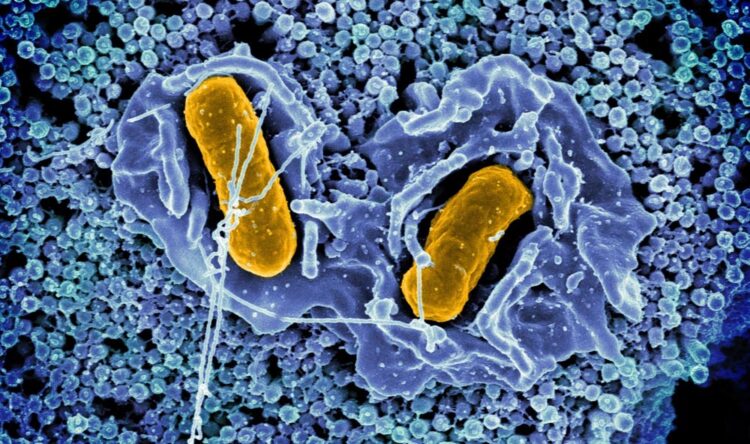
Scanning electron micrograph of Salmonella Typhimurium invading a human epithelial cell
Credit: NIAID
The immune system’s attempt to eliminate Salmonella bacteria from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract instead facilitates colonization of the intestinal tract and fecal shedding, according to National Institutes of Health scientists. The study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, was conducted by National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) scientists at Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana.
Salmonella Typhimurium bacteria (hereafter Salmonella) live in the gut and often cause gastroenteritis in people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates Salmonella bacteria cause about 1.35 million infections, 26,500 hospitalizations and 420 deaths in the United States every year. Contaminated food is the source for most of these illnesses. Most people who get ill from Salmonella have diarrhea, fever and stomach cramps but recover without specific treatment. Antibiotics typically are used only to treat people who have severe illness or who are at risk for it.
Salmonella bacteria also can infect a wide variety of animals, including cattle, pigs and chickens. Although clinical disease usually resolves within a few days, the bacteria can persist in the GI tract for much longer. Fecal shedding of the bacteria facilitates transmission to new hosts, especially by so-called “super shedders” that release high numbers of bacteria in their feces.
NIAID scientists are studying how Salmonella bacteria establish and maintain a foothold in the GI tract of mammals. One of the first lines of defense in the GI tract is the physical barrier provided by a single layer of intestinal epithelial cells. These specialized cells absorb nutrients and are a critical barrier that prevent pathogens from spreading to deeper tissues. When bacteria invade these cells, the cells are ejected into the gut lumen–the hollow portion of the intestines. However, in previous studies, NIAID scientists had observed that some Salmonella replicate rapidly in the cytosol–the fluid portion–of intestinal epithelial cells. That prompted them to ask: does ejecting the infected cell amplify rather than eliminate the bacteria?
To address this question, the scientists genetically engineered Salmonella bacteria that self-destruct when exposed to the cytosol of epithelial cells but grow normally in other environments, including the lumen of the intestine. Then they infected laboratory mice with the self-destructing Salmonella bacteria and found that replication in the cytosol of mouse intestinal epithelial cells is important for colonization of the GI tract and fuels fecal shedding. The scientists hypothesize that, by hijacking the epithelial cell response, Salmonella amplify their ability to invade neighboring cells and seed the intestine for fecal shedding.
The researchers say this is an example of how the pressure exerted by the host immune response can drive the evolution of a pathogen, and vice versa. The new insights offer new avenues for developing novel interventions to reduce the burden of this important pathogen.
###
ARTICLE:
A Chong et al. Cytosolic replication in epithelial cells fuels intestinal expansion and chronic fecal shedding of Salmonella Typhimurium. Cell Host & Microbe DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.04.017 (2021).
WHO:
Olivia Steele-Mortimer, Ph.D., chief of NIAID’s Salmonella-Host Cell Interactions Section, and Audrey Chong, Ph.D., in the Salmonella-Host Cell Interactions Section, are available to comment.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact the NIAID Office of Communications, (301) 402-1663, niaidnews@niaid.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research–at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide–to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
In a significant milestone for quantum communication technology, an experiment has demonstrated how networks can be leveraged to combat disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communications. The international effort led by researchers…

Stretchable quantum dot display
Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes achieved record-breaking performance. A team of South Korean scientists led by Professor KIM Dae-Hyeong of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for…

Internet can achieve quantum speed with light saved as sound
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute have developed a new way to create quantum memory: A small drum can store data sent with light in its sonic…





















