Virtues of modeling many faults
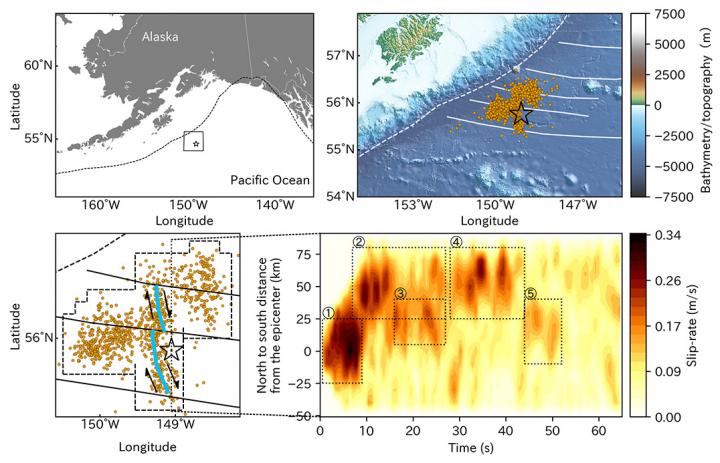
Summary of study area and result. Upper panels summarise the regional map of the study area, showing plate boundary (dashed line), seafloor fracture zones (solid lines), the epicentre (star) of the 2018 Gulf of Alaska earthquake and the aftershocks (dots). Lower-left panel show the enlarged map of our result. Blue lines are our estimate of the faults, along with the fault movements indicated as arrows. Lower-right panel shows the spatiotemporal distribution of the slip migration, projected along the north-south direction. The dashed rectangles highlight the rupture events recognised by this study.
Credit: University of Tsukuba
New method illuminates shape of Alaskan quake
A University of Tsukuba research team find that the irregular behavior of the conjugate fault system responsible for the 2018 Gulf of Alaska earthquake was linked to pre-existing features of the ocean floor.
An earthquake is generally viewed to be caused by a rupture along a fault that is transmitted outward from its point of origin in a uniform, predictable pattern. Of course, given the complexity of the environments where these ruptures typically occur, the reality is often much more complicated.
In a new study published in Scientific Reports, a research team led by the University of Tsukuba developed a new method to model the details of complex earthquake rupture processes affecting systems of multiple faults. They then applied this method to the magnitude 7.9 earthquake that struck the Gulf of Alaska near Kodiak Island on January 23, 2018.
As study co-author Professor Yuji Yagi explains, “Our method uses a flexible finite-fault inversion framework with improved smoothness constraints. This approach allows us to analyze seismic P waves and estimate the focal mechanisms and rupture evolution of geometrically complex earthquakes involving rupture of multiple fault segments.”
Based on the distribution of aftershocks within one week of the main shock of the Gulf of Alaska earthquake, this method was applied to represent slip along a horizontal plane at a depth of 33.6 km.
The main rupture stage of the earthquake, which lasted for 27 seconds, affected fault segments oriented both north-south and east-west.
“Our results confirm previous reports that this earthquake ruptured a conjugate fault system in a multi-shock sequence,” says study first author Shinji Yamashita. “Our model further suggests that this rupture tended to occur along weak zones in the sea floor: fracture zones that extend east-west, as well as plate-bending faults that run parallel to north-south-oriented magnetic lineaments.”
These features caused discontinuities in the fault geometry that led to irregular rupture behavior. “Our findings show that irregular rupture stagnation 20 kilometers north of the earthquake’s epicenter may have been promoted by a fault step across the seafloor fracture zone,” explains co-author Assistant Professor Ryo Okuwaki, “They also indicate a causal link between rupture evolution and pre-existing bathymetric features in the Gulf of Alaska.”
This method represents a promising step forward in modeling earthquake rupture processes in complex fault systems based only on seismic body waves, which may improve modeling of seismic wave propagation and mapping of complex fault networks in tectonically active areas.
###
The article, “Consecutive Ruptures on a Complex Conjugate Fault System During the 2018 Gulf of Alaska Earthquake,” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85522-w
Media Contact
Naoko Yamashina
kohositu@un.tsukuba.ac.jp
81-298-532-066
Related Journal Article
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















