USGS projects large loss of Alaska permafrost by 2100
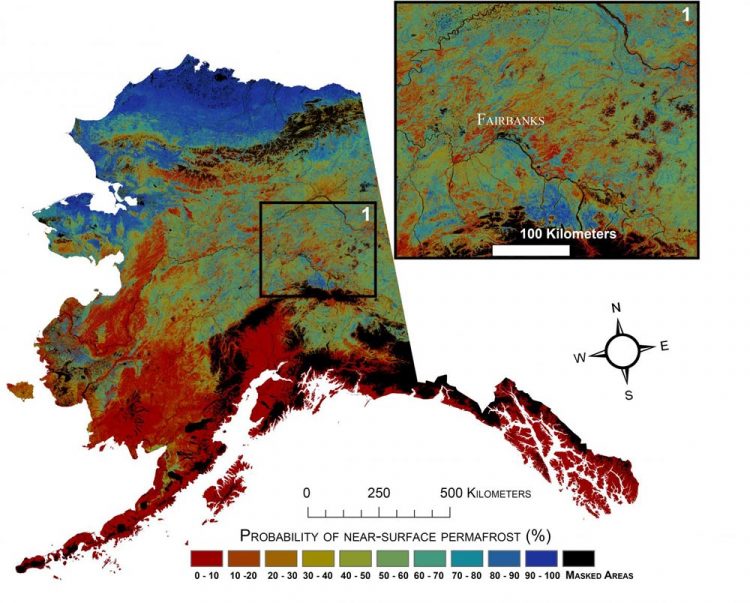
See USGS press release (link) or research article for future scenarios. Credit: USGS
Northern latitude tundra and boreal forests are experiencing an accelerated warming trend that is greater than in other parts of the world. This warming trend degrades permafrost, defined as ground that stays below freezing for at least two consecutive years.
Some of the adverse impacts of melting permafrost are changing pathways of ground and surface water, interruptions of regional transportation, and the release to the atmosphere of previously stored carbon.
“A warming climate is affecting the Arctic in the most complex ways,” said Virginia Burkett, USGS Associate Director for Climate and Land Use Change.
“Understanding the current distribution of permafrost and estimating where it is likely to disappear are key factors in predicting the future responses of northern ecosystems to climate change.”
In addition to developing maps of near-surface permafrost distributions, the researchers developed maps of maximum thaw depth, or active-layer depth, and provided uncertainty estimates. Future permafrost distribution probabilities, based on future climate scenarios produced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), were also estimated by the USGS scientists.
Widely used IPCC climate scenarios anticipate varied levels of climate mitigation action by the global community.
These future projections of permafrost distribution, however, did not include other possible future disturbances in the future, such as wildland fires. In general, the results support concerns about permafrost carbon becoming available to decomposition and greenhouse gas emission.
The research has been published in Remote Sensing of Environment. The current near-surface permafrost map is available via ScienceBase.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Machine learning algorithm reveals long-theorized glass phase in crystal
Scientists have found evidence of an elusive, glassy phase of matter that emerges when a crystal’s perfect internal pattern is disrupted. X-ray technology and machine learning converge to shed light…

Mapping plant functional diversity from space
HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration. An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong…

Inverters with constant full load capability
…enable an increase in the performance of electric drives. Overheating components significantly limit the performance of drivetrains in electric vehicles. Inverters in particular are subject to a high thermal load,…





















