The influence of the mosquito – Will malaria spread in Europe and the Mediterranean as a result of climate change?
Malaria-transmitting mosquito species will spread further in Europe in the course of this century. University of Augsburg
One aspect of climate change that has received little attention in the public debate so far is the spread of what are called vector-borne diseases, namely, diseases transmitted by a pathogen-carrying organism. These include, for example, malaria, which is transmitted by Anopheles, a species of mosquito.
The increased emergence of Anopheles-friendly weather conditions could lead to the spread of these mosquitoes and, as a result, the emergence of malaria in Europe and the Mediterranean.
Accurate predictions as to what exactly this spread might look like and how fast it could happen have not been possible hitherto. The geographer PD Dr. Elke Hertig from the University of Augsburg has now presented a model that allows a more precise evaluation.
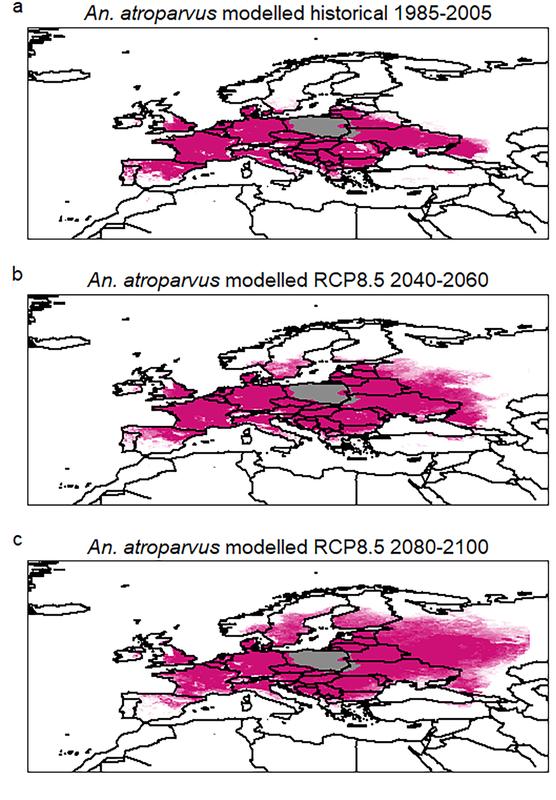
Spread northwards
With the geostatistical approach called boosted regression trees, BRT, Hertig models the occurrence of mosquitoes in Europe until the end of this century. She concludes that changes in temperature and precipitation will lead to a significant spread of malaria mosquitoes towards the north.
The expected warmer spring temperatures and the higher rainfall in summer and autumn will be especially favourable for the insects.
The most important vector is Anopheles atroparvus , the dominant malaria mosquito species in many parts of Europe, which also has the highest human bite rate and survival rate of the European Anopheles species.
Only in certain areas of the Mediterranean where precipitation is predicted to decrease will the occurrence of mosquitoes decline. The largest increases in mosquito populations towards the end of our century are expected in southern and south-eastern Europe.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-augsburg.de/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















