NASA infrared view finds small areas of strength in new depression 6E
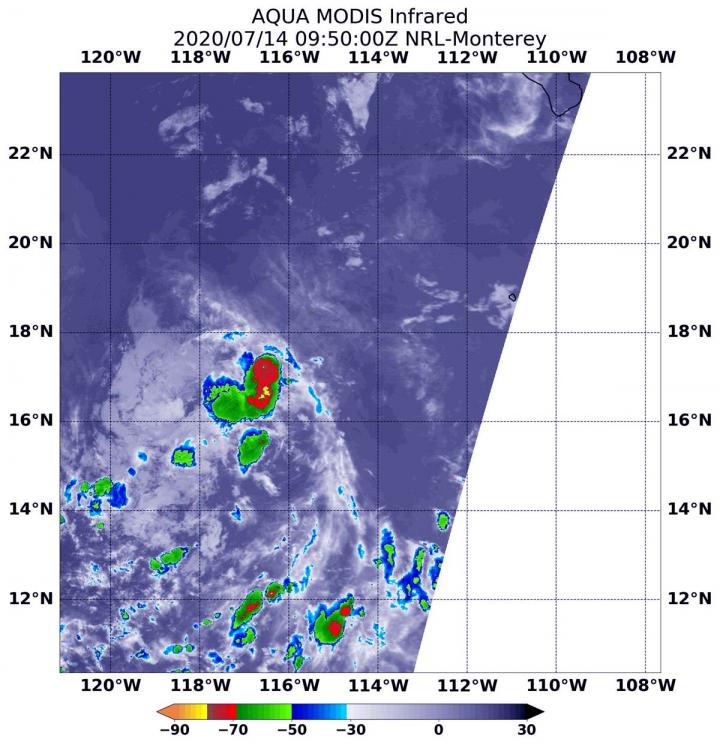
On July 14 at 5:50 a.m. EDT (0950 UTC), the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite gathered temperature information about Tropical Depression 6E's cloud tops. MODIS found a few small areas of powerful thunderstorms (red) where temperatures were as cold as or colder than minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 56.6 Celsius). Credit: NASA/NRL
Tropical Depression 6E formed in the Eastern Pacific Ocean by 5 p.m. EDT on July 13 and was located well to the southwest of Baja California Sur, Mexico.
On July 14 at 5:50 a.m. EDT (0950 UTC), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite analyzed Tropical Depression 6E's cloud tops in infrared light.
Infrared data provides temperature information, and the strongest thunderstorms that reach high into the atmosphere have the coldest cloud top temperatures.
Aqua found the most powerful thunderstorms in several small, fragmented areas northeast, southeast and southwest of the center of circulation, where temperatures were as cold as or colder than minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 56.6 Celsius).
Cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms with the potential to generate heavy rainfall. Cloud top temperatures around the rest of the depression were warmer, indicating less-powerful storms.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on July 14, the NHC said the center of Tropical Depression Six-E was located near latitude 18.1 degrees north and longitude 116.6 degrees west. 6E is far from land areas and is about 545 miles (880 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California, Mexico. The depression is moving toward the west-northwest near 16 mph (26 kph).
A faster motion toward the west-northwest or west is expected during the next day or two. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1008 millibars. Maximum sustained winds are near 30 mph (45 kph) with higher gusts. Little change in strength is forecast during the next day or two.
NHC forecaster Robbie Berg noted that, “The depression is forecast to reach waters colder than 26 degrees Celsius (78 degrees Fahrenheit) in 12 to 24 hours, which should extinguish the remaining deep convection.”
Tropical cyclones require sea surface temperatures of at least 26.6 degrees Celsius (80 degrees Fahrenheit) to maintain intensity. Therefore, the depression is expected to become a remnant low or dissipate by early Wednesday.
###
Tropical cyclones/hurricanes are the most powerful weather events on Earth. NASA's expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
For updated forecasts, visit: http://www.
By Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
More Information:
https://blogs.nasa.gov/hurricanes/2020/07/14/06e-eastern-pacific-ocean/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















