Artificial intelligence bot trained to recognize galaxies
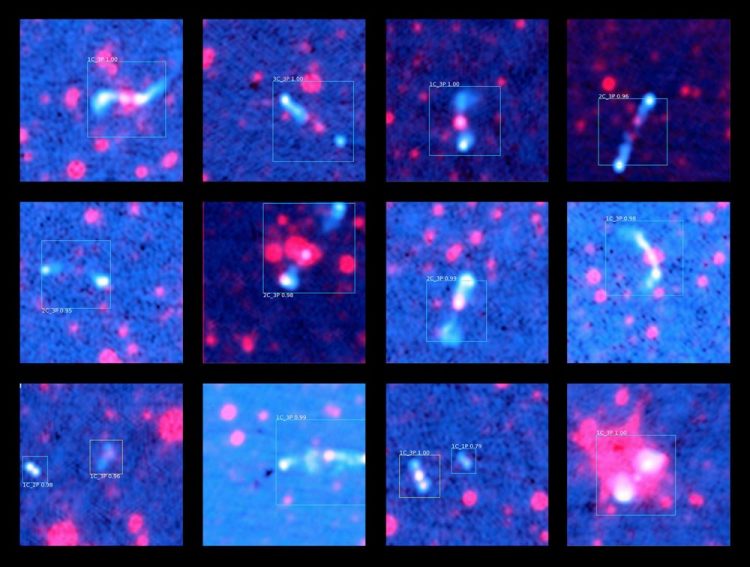
Fourteen radio galaxy predictions ClaRAN made during its scan of radio and infrared data. All predictions were made with a high 'confidence' level, shown as the number above the detection box. A confidence of 1.00 indicates ClaRAN is extremely confident both that the source detected is a radio galaxy jet system and that it has classified it correctly. Credit: Dr. Chen Wu and Dr. Ivy Wong, ICRAR/UWA
The result is an AI bot named ClaRAN that scans images taken by radio telescopes.
Its job is to spot radio galaxies–galaxies that emit powerful radio jets from supermassive black holes at their centres.
ClaRAN is the brainchild of big data specialist Dr Chen Wu and astronomer Dr Ivy Wong, both from The University of Western Australia node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR).
Dr Wong said black holes are found at the centre of most, if not all, galaxies.
“These supermassive black holes occasionally burp out jets that can be seen with a radio telescope,” she said.
“Over time, the jets can stretch a long way from their host galaxies, making it difficult for traditional computer programs to figure out where the galaxy is.
“That's what we're trying to teach ClaRAN to do.”
Dr Wu said ClaRAN grew out of an open source version of Microsoft and Facebook's object detection software.
He said the program was completely overhauled and trained to recognise galaxies instead of people.
ClaRAN itself is also open source and publicly available on GitHub.
Dr Wong said the upcoming EMU survey using the WA-based Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) telescope is expected to observe up to 70 million galaxies across the history of the Universe.
She said traditional computer algorithms are able to correctly identify 90 per cent of the sources.
“That still leaves 10 per cent, or seven million 'difficult' galaxies that have to be eyeballed by a human due to the complexity of their extended structures,” Dr Wong said.
Dr Wong has previously harnessed the power of citizen science to spot galaxies through the Radio Galaxy Zoo project.
“If ClaRAN reduces the number of sources that require visual classification down to one per cent, this means more time for our citizen scientists to spend looking at new types of galaxies,” she said.
A highly-accurate catalogue produced by Radio Galaxy Zoo volunteers was used to train ClaRAN how to spot where the jets originate.
Dr Wu said ClaRAN is an example of a new paradigm called 'programming 2.0'.
“All you do is set up a huge neural network, give it a ton of data, and let it figure out how to adjust its internal connections in order to generate the expected outcome,” he said.
“The new generation of programmers spend 99 per cent of their time crafting the best quality data sets and then train the AI algorithms to optimise the rest.
“This is the future of programming.”
Dr Wong said ClaRAN has huge implications for how telescope observations are processed.
“If we can start implementing these more advanced methods for our next generation surveys, we can maximise the science from them,” she said.
“There's no point using 40-year-old methods on brand new data, because we're trying to probe further into the Universe than ever before.”
###
A research paper on ClaRAN was released today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, published by Oxford University Press.
ICRAR
The International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) is a joint venture between Curtin University and The University of Western Australia with support and funding from the State Government of Western Australia. http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…




















