The Sun Sends Two CMEs Toward Mercury
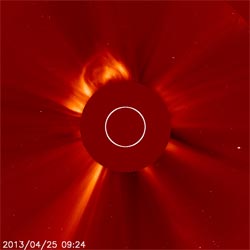
The joint ESA and NASA mission the Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) captured this series of four images of a coronal mass ejection (CME) escaping the sun on the morning of April 25, 2013. The images show the CME from 5:24 a.m. to 6:48 a.m. EDT. This was the second of two CMEs in the space of 12 hours. Both are headed away from Earth toward Mercury. Credit: ESA&NASA/SOHO <br>
Experimental NASA research models show that the first CME began at 9:30 p.m. EDT on April 24. The second CME began at 5:24 a.m. EDT on April 25. Both left the sun traveling at about 500 miles per second and they are headed in the direction of planet Mercury.
While they are not Earth-directed, the CMEs may pass by NASA’s Messenger and STEREO-A and their mission operators have been notified. There may be low levels of particle radiation associated with this event, which is what would normally concern operators of interplanetary spacecraft since the particles can trip computer electronics on board. When warranted, NASA operators can put spacecraft into safe mode to protect the instruments from the solar material.
Updates will be provided as needed.
What is a CME?
For answers to these and other space weather questions, please visit the Spaceweather Frequently Asked Questions page.
Karen C. Fox
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















