Single-atom transistor is 'perfect'
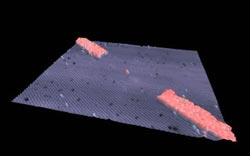
This is a single-atom transistor: 3D perspective scanning tunnelling microscope image of a hydrogenated silicon surface. Phosphorus will incorporate in the red shaded regions selectively desorbed with a STM tip to form electrical leads for a single phosphorus atom patterned precisely in the center. Credit: ARC Centre for Quantum Computation and Communication, at UNSW.<br>
The tiny electronic device, described today in a paper published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, uses as its active component an individual phosphorus atom patterned between atomic-scale electrodes and electrostatic control gates.
This unprecedented atomic accuracy may yield the elementary building block for a future quantum computer with unparalleled computational efficiency.
Until now, single-atom transistors have been realised only by chance, where researchers either have had to search through many devices or tune multi-atom devices to isolate one that works.
“But this device is perfect”, says Professor Michelle Simmons, group leader and director of the ARC Centre for Quantum Computation and Communication at UNSW. “This is the first time anyone has shown control of a single atom in a substrate with this level of precise accuracy.”
The microscopic device even has tiny visible markers etched onto its surface so researchers can connect metal contacts and apply a voltage, says research fellow and lead author Dr Martin Fuechsle from UNSW.
“Our group has proved that it is really possible to position one phosphorus atom in a silicon environment – exactly as we need it – with near-atomic precision, and at the same time register gates,” he says.
The device is also remarkable, says Dr Fuechsle, because its electronic characteristics exactly match theoretical predictions undertaken with Professor Gerhard Klimeck's group at Purdue University in the US and Professor Hollenberg's group at the University of Melbourne, the joint authors on the paper.
The UNSW team used a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) to see and manipulate atoms at the surface of the crystal inside an ultra-high vacuum chamber. Using a lithographic process, they patterned phosphorus atoms into functional devices on the crystal then covered them with a non-reactive layer of hydrogen.
Hydrogen atoms were removed selectively in precisely defined regions with the super-fine metal tip of the STM. A controlled chemical reaction then incorporated phosphorus atoms into the silicon surface.
Finally, the structure was encapsulated with a silicon layer and the device contacted electrically using an intricate system of alignment markers on the silicon chip to align metallic connects. The electronic properties of the device were in excellent agreement with theoretical predictions for a single phosphorus atom transistor.
It is predicted that transistors will reach the single-atom level by about 2020 to keep pace with Moore's Law, which describes an ongoing trend in computer hardware that sees the number of chip components double every 18 months.
This major advance has developed the technology to make this possible well ahead of schedule and gives valuable insights to manufacturers into how devices will behave once they reach the atomic limit, says Professor Simmons.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unsw.edu.auAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















