Rapid galaxy merging dominates universe’s early history

A study by an academic at The University of Nottingham gives us the first observational evidence for how massive galaxies in our universe formed.
The implications of the study are vast and are being used by astronomers to explain seemingly unrelated processes such as how massive black holes and the universe’s stars came to be.
The research, led by Dr Christopher J Conselice, of the University’s School of Physics and Astronomy, which is published in the February 20 edition of the Astrophysical Journal, uses the deepest images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope to study galaxies when they were only two billion years old. His team has found that the majority of the most massive galaxies in the early universe are undergoing multiple and spectacular mergers.
These mergers lead to the creation of new stars from colliding gas clouds and likely feed and grow the masses of black holes lurking in the centre of all galaxies.
The work is helping to definitively confirm what scientists have long hoped for — massive galaxies form when smaller galaxies merge together — a major and previously unconfirmed prediction of the cosmological standard model.
“The results show us that the most massive galaxies we see in today’s universe, which are passive and old, were once undergoing rapid mergers with each other, which it turns out is how they form,” said Dr Conselice.
While distant galaxies have been studied for over a decade, it has until now remained a mystery how they evolved into the galaxies we see today.
Young galaxies have very low masses and astronomers have long been puzzled by how these systems turn into massive galaxies in the local universe. The Conselice results demonstrate that a typical massive galaxy in today’s universe has undergone four to five mergers with other galaxies to transform from these young low mass systems into the giant galaxies.
These mergers are very rare today, with only about one per cent of galaxies merging, while 10 billion years ago, nearly all massive galaxies were undergoing mergers. An analysis technique developed by Conselice for more than 10 years was used on the deepest images ever taken of the universe to make these discoveries.
The results further show that massive galaxies did not form rapidly, within a few million years after the Big Bang, or form gradually over an extended period of time. In a surprising finding, almost all of this merger activity occurs over a very short period of time, from the birth of the universe to about six billion years ago.
Dr Conselice added: “Perhaps the most amazing thing about these results is that massive galaxy formation is largely over when the universe is half its current age. This means that all this merging activity was somehow curtailed by an unknown process.”
The research may hold clues about the formation of our own galaxy. The Milky Way contains spiral arms, which are not thought to form through the merger process. However, at the centre of our galaxy is a spherical system of stars called a bulge — a high-density region featuring many old stars and a massive black hole — which probably formed as a result of these mergers.
The research could also help astronomers to see into the Milky Way’s future — it is possible that our galaxy will itself merge with Andromeda, our nearest neighbouring large galaxy in around a billion years from now. This would see the destruction of the spiral disk that surrounds the bulge and change dramatically the shape of our galaxy, as well as significantly altering the positions of stars we see in the night sky.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nottingham.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Wildfire danger to increase due to climate change
WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research (SLF) researchers expect an elevated wildfire danger in the Alpine Foreland from 2040 onwards due to changing meteorological conditions. The danger currently remains…
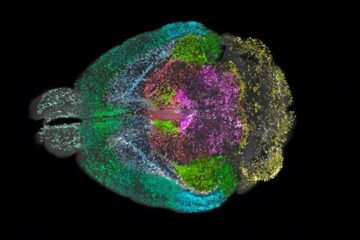
Advanced Brain Science Without Coding Expertise
Researchers at Helmholtz Munich and the LMU University Hospital Munich introduce DELiVR, offering a new AI-based approach to the complex task of brain cell mapping. The deep learning tool democratizes…
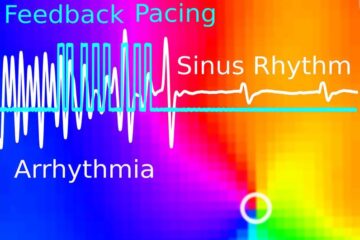
Gentle defibrillation for the heart
Using light pulses as a model for electrical defibrillation, Göttingen scientists developed a method to assess and modulate the heart function. The research team from the Max Planck Institute for…





















