A Little Chaos May Go a Long Way in Future Fusion Energy Reactors
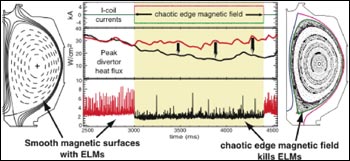
Application of ergodic magnetic field suppresses ELMs.
45th Annual Meeting of the Division of Plasma Physics
In work that makes practical, large-scale fusion energy production increasingly feasible, plasma physicists working at DOE’s DIII-D National Fusion Facility in San Diego are using a little chaos to prevent precious energy from escaping fusion energy devices.
In a magnetic fusion device, or tokamak, one of the most crucial regions for reducing the loss of heat and particles is at the plasma region’s edge. Particle crossing this edge leave the plasma, and carry energy with them, degrading the fusion reactor’s walls, and making it harder for the desired fusion energy production to occur. This problem will only increase for next-generation fusion energy machines such as the proposed ITER facility.
As the energy content of the fusion fuel increases, plasma in the edges has a tendency to become unstable, exhibiting a kind of turbulence that physicists call “Edge Localized Modes”, commonly referred to as ELMs. In experiments presented this week, an international team of researchers applied chaotic magnetic fields, in which the field lines point in unpredictable directions, to a small edge region of the plasma in the DIII-D experiment. With the chaotic magnetic field they applied, the researchers significantly reduced the ELM instabilities in the DIII-D plasma, enabling more heat to stay trapped in the fusion fuel and preserving the favorable conditions that allow fusion energy production to occur. Assuming that this approach can be extended to next-step fusion energy devices, it holds the promise of increasing the lives of materials that make up fusion-energy device walls without degrading the performance of the plasma fuel.
Contacts
T. E. Evans, General Atomics, 505-842-1234, evans@fusion.gat.com
T. S. Taylor, General Atomics, taylor@fusion.gat.com
Paul Thomas, CEA, France, paul.richard.thomas@gat.com
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















