Postcards from the plasma edge
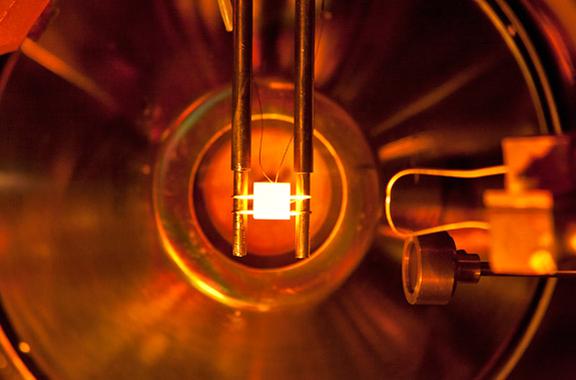
Lithium-coated molybdenum was heated to a high temperature during a PPPL experiment. Credit: Angela Capece, PPPL
Researchers have improved plasma performance by applying lithium coatings to the walls of fusion facilities. But a complete understanding of the mechanism behind this improvement remains elusive.
Among the puzzles is how temperature affects the ability of lithium to absorb and retain the deuterium particles that stray from the fuel that creates fusion reactions.
Answers are now emerging from a new surface-science laboratory at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory that can probe lithium coatings that are just three atoms thick. Such probes have examined the surface composition of lithium films on a molybdenum substrate after the films were exposed to deuterium ions.
Researchers controlled the surface temperatures, impurity levels and other conditions independently of one another, which could not be done in the complex environment of fusion devices like tokamaks.
The experiments showed that the ability of ultrathin lithium films to retain deuterium drops as the temperature of the molybdenum substrate rises — a result that provides insight into how lithium affects the performance of tokamaks.
Experiments further showed that exposing the lithium to oxygen improved deuterium retention at temperatures below about 400 degrees Kelvin. But without exposure to oxygen, the researchers found, lithium films could retain deuterium at higher temperatures as a result of lithium-deuterium bonding.
Armed with these findings, scientists will be better able to determine how to use lithium to enhance the performance of fusion plasmas.
Contact:
Angela Capece, acapece@pppl.gov
Abstract:
YI2.00005: The Effects of Temperature and Oxidation on Deuterium Retention in Solid and Liquid Lithium Films on Molybdenum Plasma-Facing Components
11:30 AM–12:00 PM, Friday, October 31, 2014
Bissonet
Session YI2: Technology of Plasma Facing Surfaces, Landau-Spitzer Award and Post Deadline Talk
9:30 AM–12:30 PM, Friday, October 31, 2014
Bissonet
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















