LZH contributing to research priority „Hybrid Numerical Optics”
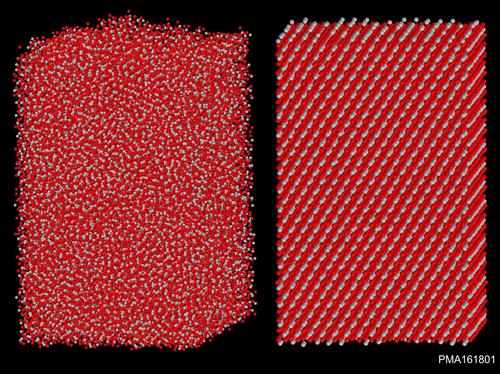
Comparison of an amorphous and a crystalline titanium oxide structure. Illustration: LZH
In the new competence center for optical simulation, the LZH is working on three subprojects in the areas of high-power glass fiber amplifiers, dielectric coatings and light propagation in fluid columns.
Highest laser powers
In the subproject „Dynamic light propagation in high output glass fiber amplifiers“, the scientists will be working on increasing the laser power of continuous and pulsed systems for the next three years. Presently, the maximum usable output power of high power fiber systems is limited by the so-called transverse mode instability (TMI).
Here, the laser beam profile begins to fluctuate above a certain output threshold. With a simulation model, the Laser Development Department at the LZH wants to more closely examine the interactions and processes in the fiber amplifier, and thus better understand TMI. Furthermore, they plan to examine another peak power dependent phenomenon, the effects of Kerr nonlinearity on the pulse propagation in fused fiber couplers.
Improving coatings
In the subproject „Structural and optical properties of dielectric coatings“, the Laser Components Department is combining different simulation techniques in order to optimize coating processes. The scientists want to understand how the coating properties and damage behavior is influenced by the coating parameters.
For this purpose, they are combining classical growth models with quantum-mechanical simulation techniques. Thus, they can determine the structural, optical and electronic properties of the coating structures produced.
Liquid-guided laser beam
In the subproject „Simulation of the light-guiding properties in coaxially flowing fluid pairs using wave-optical light propagation in fluid-dynamically and thermally superimposed refractive index distributions”, the beam guidance in flowing liquids will be simulated. The scientists in the Production and Systems Department want to predict light propagation in fluid or gaseous light waveguides using a hybrid approach. In order to do so, they will simulate a flowing liquid column using a two-fluid system.
They will also investigate the propagation of light in this liquid column. Connecting both methods is the main goal of this subproject. A liquid-guided laser beam can be used, for example, for laser materials processing.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.lzh.de/All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















