
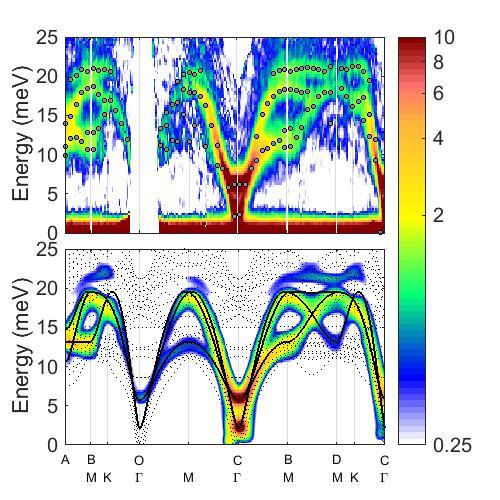
The image shows a good match between the results of the neutron scattering experiments (top) and the theoretical model (bottom).
Credit: IBS, Nature Comms
This study could provide an important breakthrough for solving a 100 year old physical problem, and deepen our knowledge of an interesting class of materials called multiferroics. The complete theoretical model and experimental observations can be read on Nature Communications.
While we generally think of solids as static objects, their molecules are actually in a constant state of vibration. These small vibrations are partly due to phonons and magnons, which are collective excitations and disturbances inside a crystal. Collective means that they are not limited to a single atom, but influence a group of neighbouring atoms. Phonons are uniform oscillations at a single frequency.
For example, short-wavelength phonons play a role in thermic conduction, while long-wavelength phonons give rise to sound, which is the origin of the word (“phonos” means voice in Greek). Magnons are collective perturbations of the electrons' spins, the compasses of the atoms. They influence the magnetic characteristics of the materials. This report shows, for the first time, that the two couple and as a consequence their vibratory behavior is not constant over time.
IBS scientists measured the atomic and molecular motion of (Y,Lu)MnO3 crystals by inelastic neutron scattering experiments and also derived a new theoretical model to explain what they observed experimentally. Interestingly, they had to go beyond the standard linear theory, which is normally used to interpret the measurements. The standard linear spin wave theory presumes that the vibration of magnons and phonons is harmonic and stable over time, like the oscillation of a spring without friction.
“Initially we used the simplest model, which is the linear spin wave theory without a coupling, but we realised that it was like the classic case of putting the elephant in the fridge: You can somehow do it, but the numbers become unrealistic and there is something wrong with it,” explains professor Park Je-Geun. “Then we did the calculations again, this time including the coupling, and we discovered that we could explain the data and, most importantly, the final analysis gave us the numbers that make sense.”
While the standard linear spin wave theory says that magnons and phonons vibrate forever and do not influence each other, a coupling would make phonons and magnons unstable, and allow an otherwise forbidden decay. For example, when a phonon becomes unstable as a consequence of the coupling to a magnon, it reduces its oscillations, decays and converts it into a magnon.
“The idea of a magnon-phonon coupling has already been around as a possible explanation for the uniquely low coefficient of thermal expansion of the invar materials. These industrially important materials have a range of uses from Swiss watches to high-speed trains, but why these materials exhibit such a counter intuitive behavior has been a puzzle for many decades,” describes the professor.
While the coupling was rarely observed before, this is the first time that it has been quantified in manganite crystal: “It is a weak coupling and present only in some materials, because it needs a particular triangular atomic architecture. It also conflicts with the mainstream belief that magnons and phonons are stable over time. This could explain why the coupling has never been carefully analyzed before, and why most scientists have ignored it,” comments the professor.
In the future, the team would like to study this coupling in other materials and ideally demonstrate that one can artificially convert phonons into magnons and vice versa.












