Growing geodesic carbon nanodomes
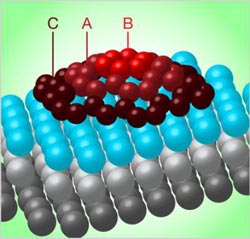
Carbon atoms form dome structures on iridium substrates, en route to forming larger scale graphene sheets. Credit: Image courtesy of Alan Stonebraker.<br>
Researchers analyzing the assembly of graphene (sheets of carbon only one atom thick) on a surface of iridium have found that the sheets grow by first forming tiny carbon domes.
The discovery offers new insight into the growth of graphene layers and points the way to possible methods for assembling components of graphene-based computer circuits.
Paolo Lacovig, Monica Pozzo, Dario Alfè, Paolo Vilmercati, Alessandro Baraldi, and Silvano Lizzit at institutions in Italy, the UK and USA report their discovery in a paper appearing October 12 in the journal Physical Review Letters. The researchers' spectroscopic study suggests that graphene grows in the form of tiny islands built of concentric rings of carbon atoms.
The islands are strongly bonded to the iridium surface at their perimeters, but are not bonded to the iridium at their centers, which causes them to bulge upward in the middle to form minuscule geodesic domes. By adjusting the conditions as the carbon is deposited on the iridium, the researchers could vary the size of the carbon domes from a few nanometers to hundreds of nanometers across.
Investigating the formation of graphene nanodomes helps physicists to understand and control the production of graphene sheets. In combination with methods for adjusting the conductivity of graphene and related materials, physicists hope to replace electronics made of silicon and metal with tiny, efficient carbon-based chips.
Jorge Sofo and Renee Diehl (Penn State University) highlight the graphene nanodome research in a Viewpoint in the October 12 issue of Physics (physics.aps.org).
Also in Physics: Clearing Up Electron Microscopy Aberrations, and Yoctosecond Flashes from Quark Gluon Plasmas
A Viewpoint by Robert Klie (University of Illinois at Chicago) describes an approach for reducing aberrations in electron microscopy, setting a new standard for low-energy imaging. And Abishek Agarwal (American Physical Society) offers a Synopsis of a model that suggests that quark-gluon plasmas produced in particle colliders could emit the briefest light bursts yet, potentially offering illumination for ultra-fast images of high speed events in atomic and molecular experiments
About APS Physics: APS Physics (physics.aps.org) publishes expert written commentaries and highlights of papers appearing in the journals of the American Physical Society.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…

A flexible and efficient DC power converter for sustainable-energy microgrids
A new DC-DC power converter is superior to previous designs and paves the way for more efficient, reliable and sustainable energy storage and conversion solutions. The Kobe University development can…





















