A quantum connection between light and mechanics
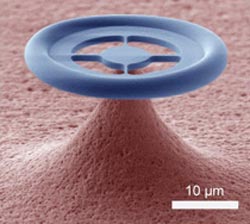
Electron microscopy image of the glass donut, which is smaller than the diameter of a hair. It is connected to the supporting chip by four spokes, to ensure that the structure can vibrate for a long time like a good tuning fork. Light can circulate up to a million times around the circumference of the donut. As the light bounces against the walls of the structure, it exerts a small force on the glass, which can influence the vibrations of the structure. © K-Lab/EPFL<br>
Researchers supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) have demonstrated a microscopic system in which light can be converted into a mechanical oscillation and back. This interaction is so strong that it becomes possible to control the motion of the oscillator at the level where quantum mechanics governs its behaviour.
Since the early 20th century, it is known that the movement of objects is ultimately governed by the laws of quantum mechanics, which predict some intriguing phenomena: An object could simultaneously be in two places at the same time, and it should always be moving a little, even at a temperature of absolute zero – the oscillator is then said to be in its quantum ground state. Yet we never experience such behaviour in the things we see around us and interact with in daily life.
Quantum strangeness
Indeed, quantum effects can only be observed on very well isolated systems, where the coupling to the surrounding environment is extremely weak. For large objects, the unavoidable coupling quickly washes out the quantum properties, in a process known as decoherence. Until recently, scientists were only able to observe quantum mechanical traits in the motion of tiny systems, such as single atoms or molecules. Now, a team of physicists in the EPFL’s Laboratory of Photonics and Quantum Measurement directed by Tobias Kippenberg has shown that it is possible to control the motion of an object, sufficiently large to be seen with the naked eye, at the level where quantum mechanics dominates. They achieve this by illuminating the object with laser light. The results are published in this week’s edition of Nature magazine*.
A ring of light
The structure is a carefully crafted glass donut on a microchip, with a diameter of 30 micrometres (about one half of a hair’s diameter) which can vibrate at a well-defined frequency. At the same time, it acts as a racetrack for light, which can circle around the circumference of the donut. In turning the bend, the light exerts a little force on the glass surface, an effect called 'radiation pressure'. Although this force is very small, in these structures it can become appreciable since light circles around the structure up to a million times before being lost. The radiation pressure force can make the ring move, causing it to vibrate like a finger running along the rim of a wineglass. But it can in fact also dampen the vibrations, and thus cool down the oscillatory motion.
Cold, colder, …
Cooling is crucial to reaching the regime of quantum mechanical motion, as this is normally overshadowed by random thermal fluctuations. For this reason, the structure is brought to a temperature of less than one degree above absolute zero. Radiation pressure damping by laser light launched into the donut then cools the motion down by an extra factor 100. The oscillator is cooled so much that it spends a large fraction of the time in its quantum ground state. But even more importantly: The interaction between light and the movement of the oscillator can be made so strong that the two form an intimate connection. A small excitation in the form of a light pulse can fully transform into a small vibration and back again. For the first time, this transformation between light and motion is made to occur within a time that is short enough such that the quantum properties of the original light pulse are not lost in the process through decoherence. By outpacing decoherence, the current results provide a powerful way to control the quantum properties of the oscillator motion, and see the peculiar predictions of quantum mechanics at play in human-made objects.
* E. Verhagen, S. Deléglise, S. Weis, A. Schliesser and T. J. Kippenberg (2012). Quantum-coherent coupling of a mechanical oscillator to an optical cavity mode. Nature online DOI: 10.1038/nature10787
(available as a pdf-file from the SNSF; e-mail: com@snf.ch)
Contact:
Professor Tobias Kippenberg
Laboratory of Photonics and Quantum Measurements
EPFL
CH-1015 Lausanne
E-mail: tobias.kippenberg@epfl.ch
Tel: +41 (0)21 693 44 28
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















