A potentially revolutionnary material: scientists produce a novel form of artificial graphene
Artifical graphene<br>Physics and Materials Science Research Unit<br>
”Artificial graphene” should lead to faster, smaller and lighter electronic and optical devices of all kinds, including higher performance photovoltaic cells, lasers or LED lighting.
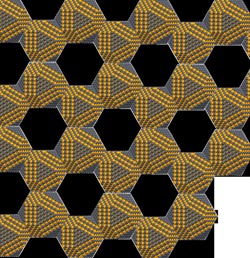
For the first time, scientists are able to produce and have analysed artificial graphene from traditional semiconductor materials. Such is the scientific importance of this breakthrough these findings were published recently in one of the worldfs leading physics journals, Physical Review X. A researcher from the University of Luxembourg played an important role in this highly innovative work.
Graphene (derived from graphite) is a one atom thick honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms. This strong, flexible, conducting and transparent material has huge scientific and technological potential. Only discovered in 2004, there is a major global push to understand its potential uses. Artificial graphene has the same honeycomb structure, but in this case, instead of carbon atoms, nanometer-thick semiconductor crystals are used. Changing the size, shape and chemical nature of the nano-crystals, makes it possible to tailor the material to each specific task.
The University of Luxembourg is heavily involved in cross-border, multidisciplinary research projects. In this case it partnered with the Institute for Electronics, Microelectronics, and Nanotechnology (IEMN) in Lille, France, the Debye Institute for Nanomaterials Science and the Institute for Theoretical Physics of the University of Utrecht, Netherlands and the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden, Germany.
University of Luxembourg researcher Dr. Efterpi Kalesaki is the first author of the article appearing in the Physical Review X . Dr. Kalesaki said: ”these self]assembled semi-conducting nano-crystals with a honeycomb structure are emerging as a new class of systems with great potential.” Prof Ludger Wirtz, head of the Theoretical Solid-State Physics group at the University of Luxembourg, added: ”artificial graphene opens the door to a wide variety of materials with variable nano]geometry and etunablef properties.”
About the Physics and Materials Science Research Unit
The Physics and Materials Science Research Unit of the University of Luxembourg focuses on condensed matter physics. Its activities cover the whole field from the electronic structure of crystals to the thermodynamics of soft matter. Experimental and theoretical groups join forces to understand and develop materials.
Weitere Informationen:
http://prx.aps.org/abstract/PRX/v4/i1/e011010
– Link to the scientific article
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni.luAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Rocks with the oldest evidence yet of Earth’s magnetic field
The 3.7 billion-year-old rocks may extend the magnetic field’s age by 200 million years. Geologists at MIT and Oxford University have uncovered ancient rocks in Greenland that bear the oldest…

Decisive breakthrough for battery production
Storing and utilising energy with innovative sulphur-based cathodes. HU research team develops foundations for sustainable battery technology Electric vehicles and portable electronic devices such as laptops and mobile phones are…

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…





















