Using nanoparticles to combat arteriosclerosis
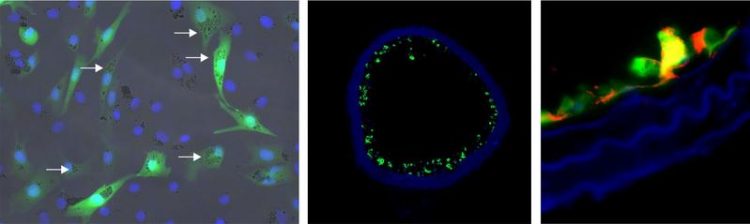
Fluorescence-labeled cells with nanoparticles Photo: Dr. Sarah Rieck/Dr. Sarah Vosen/University of Bonn
In arterial calcification (arteriosclerosis), pathological deposits form in the arteries and this leads to vascular stenosis. Strokes and heart attacks are a frequent outcome due to the resultant insufficient blood flow.
Endothelial cells which line the blood vessels play an important role here. “They produce nitric oxide and also regulate the expansion of the vessels and the blood pressure,” explains junior professor Dr. med. Daniela Wenzel from the Institute of Physiology I of the University of Bonn. Damage to the endothelial cells is generally the insidious onset of arteriosclerosis.
A team of researchers working with Jun.-Prof. Wenzel, together with the Technische Universität München, the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University of Bonn Hospital and the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Berlin, developed a method with which damaged endothelial cells can regenerate and which they successfully tested in mice.
The scientists transferred the gene for the enzyme eNOS into cultured cells with the aid of viruses. This enzyme stimulates nitic oxide production in the endothelium like a turboloader. “The enzyme is an essential precondition for the full restoration of the original function of the endothelial cells,” reports Dr. Sarah Vosen from Jun.-Prof. Wenzel's team.
A magnet delivers the nanoparticles to the desired site
Together with the gene, the scientists also introduced tiny nanoparticles, measuring a few hundred nanometers (one-millionth of a millimeter), with an iron core. “The iron changes the properties of the endothelial cells: They become magnetic,” explains Dr. Sarah Rieck from the Institute of Physiology I of the University of Bonn.
The nanoparticles ensure that the endothelial cells equipped with the “turbo” gene can be delivered to the desired site in the blood vessel using a magnet where they exert their curative effect. Researchers at the Technische Universität München have developed a special ring-shaped magnet configuration for this which ensures that the replacement cells equipped with nanoparticles line the blood vessel evenly.
The researchers tested this combination method in mice whose carotid artery endothelial cells were injured. They injected the replacement cells into the artery and were able to position them at the correct site using the magnet.
“After half an hour, the endothelial cells adhered so securely to the vascular wall that they could no longer be flushed away by the bloodstream,” says Jun.-Prof. Wenzel. The scientists then removed the magnets and tested whether the fresh cells had fully regained their function. As desired, the new endothelial cells produced nitric oxide and thus expanded the vessel, as is usual in the case of healthy arteries. “The mouse woke up from the anesthesia and ate and drank normally,” reported the physiologist.
Transfer to humans requires additional research
Normally, doctors surgically remove vascular deposits from the carotid artery and in some cases place a vascular support (stent) to correct the bottleneck in the crucial blood supply. “However, these areas frequently become blocked with deposits once again,” reports Jun.-Prof. Wenzel.
“In contrast, we are getting to the root of the problem and are restoring the original condition of healthy endothelial cells.” The researchers hope that what works in mice is also possible in humans, in principle. However, there are still many challenges to overcome. Jun.-Prof. Wenzel: “There is still a considerable need for research.”
The study was supported by funding to the junior research group “Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) – endothelial cell replacement in injured vessels” by the State of North Rhine-Westphalia and to the DFG Research Unit FOR 917 “Nanoguide”.
Publication: Vascular repair by circumferential cell therapy using magnetic nanoparticles and tailored magnets, journal “ACS NANO”, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b04996
Detailed image caption: On the left are fluorescence-labeled cells with nanoparticles: The cellular nuclei are shown in blue, the fluorescence labeling is shown in green and the nanoparticles in the cells are identified by arrows. The middle photo shows a blood vessel populated with these cells (green). On the right is a detailed image of a vascular wall with the eNOS protein identified (red). © Photo: Dr. Sarah Rieck/Dr. Sarah Vosen/University of Bonn
Media contact information:
Junior professor Dr. med. Daniela Wenzel
Institute of Physiology I
University of Bonn
Tel. 0228/6885216
E-Mail: dwenzel@uni-bonn.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-bonn.deAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















