Brain Imaging Study Reveals Placebo’s Effect
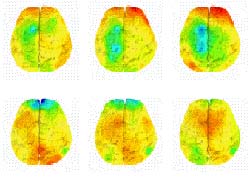
Image: Courtesy of Andrew Leuchter et al.
Scientists have recognized for some time that people suffering from depression often experience a substantial reduction in symptoms when given a placebo. In fact, this observation has led some researchers to propose that up to 75 percent of the apparent efficacy of antidepressant medicine may actually be attributable to the placebo effect. Determining the cause of a patient’s improvement under such circumstances is no easy task. But the results of a new study may shed light on the matter. According to a report in the January issue of the American Journal of Psychiatry, depressed patients who respond to placebo treatment do exhibit a change in brain function, but one that differs from that seen in patients who respond to medication.
Using so-called quantitative electroencephalography imaging, a team of researchers at the University of California at Los Angeles studied electrical activity in the brains of 51 depressed patients receiving either placebo treatment or active medication. Patients who responded favorably to the placebo, the investigators found, showed increased activity in a region of the brain known as the prefrontal cortex. Those who responded to medication, in contrast, exhibited suppressed activity in that area. The image shown here illustrates changes in prefrontal cortex activity over time in the placebo responders group (top row) and the medication responders group (bottom row), with red indicating an increase in activity and blue-green representing a decrease. “Both treatments affect prefrontal brain function,” the researchers write, “but they have distinct effects and time courses.”
These results “show us that there are different pathways to improvement for people suffering from depression,” team member Andrew Leuchter notes. “Medications are effective, but there may be other ways to help people get better,” he adds. “If we can identify what some of the mechanisms are that help people get better with placebo, we may be able to make treatments more effective.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.sciam.com/news/010202/1.htmlAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















