How Memory and Schizophrenia are Connected
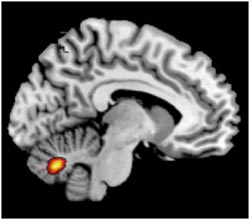
Activation of voltage-gated ion channels in the cerebellum. (Illustration: MCN)<br>
The ability to hold transitory information – e.g. memorizing a telephone number – is a fundamental function of the human brain. This so-called working memory enables us to understand the world that surrounds us.
To keep the working memory running, our brain uses a lot of energy, however, in many psychiatric disorders working memory is disturbed. Scientists of the Transfaculty Research Platform “Molecular and Cognitive Neurosciences” (MCN) at the University of Basel and the Psychiatric University Clinics have now described a network of genes that controls fundamental properties of neurons and is related to working memory, brain activity and schizophrenia.
Ion channels as key players
In the current study, Angela Heck analyzed the genetic basis of working memory in over 2800 healthy participants across different age groups. She then used bioinformatics methods in order to identify biologically meaningful groups of genes. The analysis revealed that one group of genes, the group of voltage-gated ion channels, was of particular relevance. These molecules are regulating a very basic property of neurons: their electric excitability. The same method was also applied to a population of over 32.000 participants, made up of both patients suffering from schizophrenia and healthy participants. Again, the ion channels belonged to the gene group with the strongest genome-wide effects.
In a further step, Matthias Fastenrath studied the brain activity of 700 healthy participants via functional imaging while they were were solving working memory tasks. The group of genes of the ion channels correlated strongly with the activity of two brain regions in the cerebrum and the cerebellum. Earlier studies have shown that these two brain regions are important for a functioning working memory. Molecules regulating the electric excitability of neurons are thus important for human working memory and neural processes of defined regions. Malfunctions of this mechanism may also contribute to the development of schizophrenia.
Starting point for drug development
The results of this study contribute to the understanding of the molecular basis of memory processes and psychiatric disorders. The findings provide a good starting point for the development of drugs aimed at treating memory-related and psychiatric disorders.
The Transfaculty Research Platform MCN is a joint endeavor of the Faculty of Psychology at the University of Basel and the Psychiatric University Clinics. Its goal is to advance research on the neurobiological underpinnings of human emotional and cognitive processes and to contribute to the development of novel treatment options for neuropsychiatric disorders. Human genetics and functional imaging are the methodological backbone of MCN’s research. The platform is jointly led by Prof. Dominique de Quervain and Prof. Andreas Papassotiropoulos.
Orignial source
Heck, A., Fastenrath, M., Ackermann, S., Auschra, B., Bickel, H., Coynel, D., Gschwind, L., Jessen, F., Kaduszkiewicz, H., Maier, W., Milnik, A., Pentzek, M., Riedel-Heller, S.G., Ripke, S., Spalek, K., Sullivan, P., Vogler, C., Wagner, M., Weyerer, S., Wolfsgruber, S., de Quervain, D.J.F., Papassotiropoulos, A.
Converging genetic and functional brain imaging evidence links neuronal excitability to working memory, psychiatric disease, and brain activity.
Neuron, online | DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.010
Further information
Prof. Dr. med. Andreas Papassotiropoulos, Transfaculty Research Platform “Molecular and Cognitive Neuroscience”, Faculty of Psychology at the University of Basel and the Psychiatric University Clinics, phone: +41 (0)61 267 05 99, email: andreas.papas@unibas.ch
Weitere Informationen:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0896627314000154
– Abstract
https://mcn.unibas.ch
– Transfaculty Research Platform “Molecular and Cognitive Neurosciences” (MCN)
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















