A novel motion tracking system assesses functional rehabilitation of the upper limbs
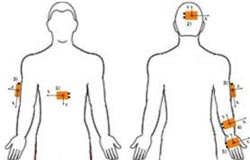
The sensors were located on the trunk (1), the back of the head (2), the right arm (3), the forearm (4) and the hand (5).<br><br>Credit: Neural Regeneration Research<br>
The most common assessment tools are based on rating scales, which are inefficient when measuring small changes and can yield subjective bias. An objective quantification of patient performance during rehabilitation can be achieved using instruments to capture motion trajectories and specific details of task execution.
Various commercial systems use different sensor technologies to accurately track human motion. Electromagnetic motion capture systems have been widely used to track human movements in virtual reality applications.
While the problem of marker occlusion does not arise with these systems, the electromagnetic fields they use are subjected to interference and are affected by metallic objects. Ángel Gil-Agudo and colleagues from National Hospital for Spinal Cord Injury of Spain designed an inertial sensor-based monitoring system and developed a kinematic model with nine degrees of freedom to analyze upper limb and head movements in three dimensions.
This system was then validated using a commercial optoelectronic system. These findings, published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 8, No. 19, 2013), suggest that an inertial sensor-based motion tracking system can be used in patients who have upper limb impairment through data integration with a virtual reality-based neurorehabilitation system.
Article: ” A novel motion tracking system for evaluation of functional rehabilitation of the upper limbs,” by Ángel Gil-Agudo1, Ana de los Reyes-Guzmán1, Iris Dimbwadyo-Terrer1, Benito Peñasco-Martín1, Alberto Bernal-Sahún2, Patricia López-Monteagudo2, Antonio del Ama-Espinosa1, José Luis Pons3 (1 Department of Biomechanics and Technical Aids, National Hospital for Spinal Cord Injury, Toledo, Spain; 2 Health Department, Indra Systems, Alcobendas, Madrid, Spain;3 Bioengineering Group, Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), Arganda del Rey, Madrid, Spain)
Gil-Agudo Á, de los Reyes-Guzmán A, Dimbwadyo-Terrer I, Peñasco-Martín B, Bernal-Sahún A, López-Monteagudo P, del Ama-Espinosa A, Pons JL. A novel motion tracking system for evaluation of functional rehabilitation of the upper limbs. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(19):1773-1782.
Contact:
Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















