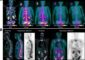
Study shows balloon pump use prior to angioplasty does not reduce heart muscle damage

The findings were published online today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), and presented at the European Society of Cardiology in Paris, France.
The intra-aortic balloon pump works by increasing the blood supply to the heart, which reduces the heart's workload. According to Manesh Patel, M.D., the principal investigator and cardiologist at the Duke Clinical Research Institute (DCRI), “animal studies had suggested that inserting a balloon pump before opening the vessel would reduce the heart's workload and by doing so, could potentially reduce infarct size When we tested this observation in humans, we did not show an infarct reduction.”
CRISP AMI was a multi-center, prospective, randomized trial that enrolled patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) without shock within six hours of chest pain onset and planned primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Of the 337 patients enrolled, 161 were randomized to receive intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation (IABC) prior to primary PCI, and 176 to the standard of care (SOC), which is primary PCI without IABC support.
The mean infarct size, measured using cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, was not significantly different between the IABC and SOC groups (42.1% vs. 37.5%). At 30 days, major bleeding or transfusion occurred in 5 (3.1%) of the IABC patients versus 3 (1.7%) of SOC patients. Major vascular complications occurred in 7 (4.3%) of the IABC patients, versus 2 (1.1%) of the SOC patients. treated with IABC compared to SOC. By six months, death occurred in 3 (1.9%) in the IABC group and 9 (5.2%) in the SOC group.
While the study was not set up to report clinical events, the researchers say the results are interesting because they offer unique insight into treating AMI patients.
“The most striking observation is the excellent overall outcome for the highest-risk patients within the context of this trial,” says E. Magnus Ohman, M.D., a co-investigator and cardiologist at DCRI. “The IABC group had less than five percent mortality. It's hard to improve that. We've gotten very good at treating AMI patients.”
Acute myocardial infarction patients represent nearly half of the approximately 1.5 million annual hospitalizations for acute coronary syndromes in the U.S. Acute mortality risk is between 6% and 15%; one-year mortality is estimated at 38% for women and 25% for men.
Ohman says it's also important to note that 15 of the patients in the standard of care group crossed over to receive IABC – five prior to PCI and 10 after.
“While routine use of IABC is not recommended, physicians should be vigilant about identifying patients who are at risk for rapid deterioration and may benefit from counterpulsation,” says Patel.
Funding for CRISP AMI was provided by Maquet/Datascope.
Manesh Patel, M.D., receives research grants and support from Maquet/Datascope.
Co-authors of this paper include Richard W. Smalling, M.D. Ph.D, Memorial Hermann Heart and Vascular Institute, University of Texas, Houston, TX;Holger Thiele, M.D., University of Leipzig-Heart Center, Leipzig, Germany; Huiman X. Barnhart, Ph.D. and Yi Zhou, Ph.D, DCRI; Praveen Chandra, M.D., Medanta–The Medicity, Haryana, India; Derek Chew, M.D., Flinders Medical Center, Bedford Park, Australia; Marc Cohen, M.D., Newark Beth Israel Medical Center, Newark, NJ; John French, MB, CHB, Ph.D., Liverpool Hospital, Liverpool, Australia; and Divaka Perera, M.D., Kings College, London, UK.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.duke.eduAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…