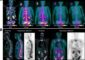
Researchers’ New Method May Sharpen Microscopic Images

Electrical engineering professor Dr. Raimund Ober and his team recently published their findings in the journal Nature Methods. In the journal, they describe a method which minimizes the deterioration of images that can occur with conventional imaging approaches.
“Any image you take of an object is translated by the camera into pixels with added electronic noise,” Ober said. “Any distortion of an image makes it harder to obtain accurate estimates of the quantities you’re interested in.”
This method could greatly enhance the accuracy with which quantities of interest, such as the location, size, and orientation of an object, are extracted from the acquired images.
Ober and his team tackled this problem by using the EMCCD camera (a standard low-light image detector) in a highly unconventional setting. Using this method, scientists can estimate quantities of interest from the image data with substantially higher accuracy than those made with conventional low-light imaging.
“We have figured out through rigorous theoretical developments that when you run an EMCCD camera in such a way that very few photons hit each of its pixels, the resulting image is minimally corrupted by the camera noise,” he said. “Our method is about using the EMCCD camera to its fullest potential, beyond what is commonly believed to be possible by the scientific imaging community.”
By increasing the magnification of the image to reduce the number of photons detected in each image pixel, they were able to significantly reduce the camera noise and considerably lessen the deteriorative effect of pixilation.
In fact, the team managed to attain particle localization accuracy that was twofold higher than those obtained with conventional EMCCD imaging.
Ober and his team applied UAIM (Ultrahigh Accuracy Imaging Modality) to the live-cell tracking of a standard protein marker for breast cancer. By being able to accurately follow the movement of the marker, valuable insights on the biology of breast cancer could be gained.
“The tracking of individual proteins represents an important way to study cancer and other diseases at the molecular level,” Ober said. “The applications of UAIM for diagnostics and research are promising.”
The research team included Jerry Chao and Sripad Ram, post-doctoral researchers at UT Dallas, and Dr. Sally Ward, professor of immunology at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas.
Media Contact: Katherine Morales, 972-883-4321, kxm109320@utdallas.edu
or the Office of Media Relations, 972-883-2155, newscenter@utdallas.edu
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.utdallas.eduAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…