Making virtopsies a reality

A new research project at the University of Leicester is set to play a vital role in continuing research into viable alternatives to invasive autopsies, which many families find to be unpleasant.
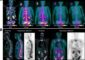
The research team at the University of Leicester’s East Midlands Forensic Pathology Unit has won a substantive award by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) to investigate and develop the use of cardiac angiography in relation to near virtual autopsies.
Currently, diagnoses such as coronary heart disease cannot be made by using CT scans. It is hoped that this new project will develop a reliable and cost-effective system which can be used to diagnose coronary heart disease from CT scans. The technology will be used to visualise coronary arteries in cadavers and make a diagnosis comparable to current autopsy practice.
The research is a collaborative project between researchers in the East Midlands Forensic Pathology Unit at the University of Leicester and researchers in the Imaging Department at the University Hospitals of Leicester. The project officially began at the beginning of June and will run for 18 months.
Professor Guy Rutty, who is heading up the project, commented:
“The outcome of this research has the potential to affect every family in the future, and is a significant contribution to the developing practice of using CT scans instead of autopsies. We are investigating a realistic alternative to the autopsy and are confident we can produce a reliable and cost-effective system which can be used in the future as an alternative to the invasive autopsy.”
Notes to Editors
For more information about this research, please contact Professor Guy Rutty on 0116 252 3221 or via email at gnr3@le.ac.uk
The project is funded by the NIHR Research for Innovation, Speculation and Creativity (RISC) programme.
About NIHR:
The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) provides the framework through which the research staff and research infrastructure of the NHS in England is positioned, maintained and managed as a national research facility. The NIHR provides the NHS with the support and infrastructure it needs to conduct first-class research funded by the Government and its partners alongside high-quality patient care, education and training. Its aim is to support outstanding individuals (both leaders and collaborators), working in world-class facilities (both NHS and university), conducting leading-edge research focused on the needs of patients. www.nihr.ac.uk
Press Office Contact:
Ather Mirza
Press Office
Division of Marketing, Planning & Communications
University of Leicester
LE1 7RH
Tel: 0116 252 3335
Email: pressoffice@le.ac.uk
Twitter: @UniofLeicsNews
ABOUT THE UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
– A member of the 1994 Group of universities that shares a commitment to research excellence, high quality teaching and an outstanding student experience.
Winner of Outstanding Student Support award, Times Higher 2009/10
Named University of the Year by Times Higher (2008/9) Shortlisted (2006, 2005) and by the Sunday Times (2007)
Ranked top with Cambridge for student satisfaction amongst full time students taught at mainstream universities in England
Ranked as a Top 20 UK university by the Sunday Times, Guardian, and Times
Ranked in world’s top 3% of universities by Shanghai Jiao Tong International Index, 2005-08 and the Times Higher Education-QS World University Rankings
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www2.le.ac.uk/about/factsAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…