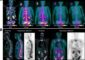
Johns Hopkins GI doctors use endoscopy to place transpyloric stent

Physicians at Johns Hopkins say they are encouraged by early results in three patients of their new treatment for gastroparesis, a condition marked by the failure of the stomach to properly empty its contents into the small intestine.
In an article published online today in the journal Endoscopy, they describe how the placement of a small metal stent in the stomach can improve life for people who suffer from severe bouts of nausea, abdominal pain and vomiting that accompany the condition.
John Clarke, M.D., assistant professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and the article's lead author, used an endoscope to place a pyloric stent in three patients with delayed gastric emptying. The pylorus is the part of the stomach that connects to the small bowel.
“I think this new technique could play a big role in the treatment of gastroparesis,” says Clarke, who also is clinical director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Neurogastroenterology. “Though it sounds a little bit unconventional, the safety of it may be better than anything else we have out there.”
Clarke says recently developed flexible, silicone-covered metal stents have already been approved to treat some gastrointestinal obstructions, but until now have not been used to treat gastroparesis.
Typically, patients with gastroparesis don't get a lot of good news from their physicians. Stomach surgery or risky medications such as erythromycin and metoclopramide have been the go-to treatments for the condition, which can have serious health and quality-of-life consequences.
“There are few FDA-approved options for gastroparesis patients,” Clarke says. “The only medicines that are approved have a number of adverse effects associated with them.”
The National Institutes of Health estimates that 5 million Americans live with gastroparesis, a condition in which the contents of the stomach empty into the intestine slowly or not at all. Symptoms, including reflux, become chronic.
Using an endoscope, Clarke placed a self-expandable, coated metallic stent across the three patients' pyloric channels, holding the channels open and allowing the patients' stomachs to empty normally.
All three patients showed dramatic reductions in symptoms, Clarke says. One was a 15-year-old boy with chronic nausea and vomiting who had endured unsuccessful trials of erythromycin, metoclopramide, domperidone and promethazine. A second was a 54-year-old man with idiopathic gastroparesis who also didn't respond to medication, but had complete recovery after his stent placement. In a third patient, the stent migrated out of place and her pain came back, but after replacing it, the pain eased, Clarke reports. All were treated at The Johns Hopkins Hospital.
Clarke says the stent placement procedure isn't difficult.
“Technically it's pretty simple, and the risk appears to be minimal; if it doesn't work, you just take it out,” he says. “Gastric surgery to stimulate emptying is riskier than endoscopy.”
The number of patients diagnosed with gastroparesis is on the rise, Clarke says. “I'd estimate that 30 percent of my clinical practice comprises patients with gastroparesis.”
Clarke says a larger clinical trial, which he expects to begin in the near future, is needed to provide longer follow-up of results and to identify which patients are likely to benefit the most from stents. “Our hope is that stent placement may become either a primary treatment option or a bridge technology to determine who can best benefit from surgery to improve stomach emptying.”
Johns Hopkins Medicine (JHM), headquartered in Baltimore, Maryland, is a $6.7 billion integrated global health enterprise and one of the leading health care systems in the United States. JHM unites physicians and scientists of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine with the organizations, health professionals and facilities of The Johns Hopkins Hospital and Health System. JHM's mission is to improve the health of the community and the world by setting the standard of excellence in medical education, research and clinical care. Diverse and inclusive, JHM educates medical students, scientists, health care professionals and the public; conducts biomedical research; and provides patient-centered medicine to prevent, diagnose and treat human illness. JHM operates six academic and community hospitals, four suburban health care and surgery centers, more than 38 primary health care outpatient sites and other businesses that care for national and international patients and activities. The Johns Hopkins Hospital, opened in 1889, was ranked number one in the nation for 21 years by U.S. News & World Report.
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Media Relations and Public Affairs
Media Contacts:
Patrick Smith
410-955-8242
psmith88@jhmi.edu
or
Helen Jones
410-502-9422
hjones49@jhmi.edu
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.jhmi.eduAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…