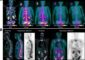
Diagnosing breast cancer using red light
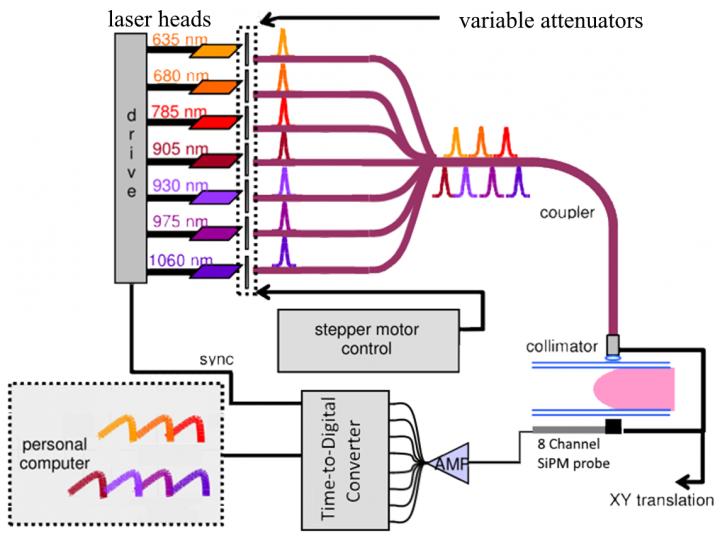
Schematic Diagram for OM Instrument: Seven pulsed lasers sequentially illuminate the compressed breast; transmitted light is detected by the 8-channel SiPM probe and the TDC acquires the signal. Credit: Edoardo Ferocino
Optical Mammography, or OM, which uses harmless red or infrared light, has been developed for use in conjunction with X-rays for diagnosis or monitoring in cases demanding repeated imaging where high amounts of ionizing radiation should be avoided. At the OSA Biophotonics Congress: Biomedical Optics meeting, held 3-6 April in Hollywood, Florida, USA, researchers from Milan, Italy, will report an advance in instrument development that increases the sensitivity of OM by as much as 1000-fold.
In 2012, the most recent year for which data is available, more than 1.7 million women worldwide were diagnosed with breast cancer. Many of these diagnoses are made using X-ray mammography. Although standard and widely used, X-ray imaging for breast cancer suffers from both low sensitivity (50-75%) and the use of ionizing radiation that cannot be considered completely safe.
The newly-developed instrument replaces two photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) of existing instruments with an eight-channel probe involving silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs) and a multichannel time-to-digital converter. These changes eliminate a time-wasting pre-scan step that was required to avoid damage to the PMTs. In addition to increased sensitivity, the new instrument is both more robust and cheaper.
While X-ray mammography is widely used and is still the recommended method for routine screenings, its use is limited by the patient's age, weight or body mass index, whether or not hormone replacement therapy is being used, and other issues. In addition, its accuracy — particularly when used in younger women — has been called into question. Other imaging techniques, such as MRI and ultrasound, are sometimes suggested, but neither is an effective replacement for X-ray mammography.
Optical imaging methods, on the other hand, have attracted increasing interest for breast cancer diagnosis since both visible and infrared light are highly sensitive to blood volume and oxygenation. Tumors are characterized by a high volume of blood due to the increased vascularization that occurs as tumors grow. OM can be used to measure blood volume, oxygenation, lipid, water and collagen content for a suspicious area identified through standard X-ray imaging. Collagen measurements are particularly important since this species is known to be involved in the onset and progression of breast cancer.
One major disadvantage to OM imaging is the poor spatial resolution that has been achieved to date. Breast cancer tumors larger than 1 centimeter are very dangerous and more likely to lead to death, so a successful screening technique must be able to resolve smaller lesions. This remains a problem with OM imaging as a stand-alone technique, but combining OM with other imaging methods shows some promise.
A possible advantage to OM, however, is that only gentle pressure need be applied to the breast tissue, in stark contrast to the standard technique for X-ray imaging. In fact, breast compression tends to reduce blood volume in the tissue, which would interfere with the OM image, so some three-dimensional OM detectors being developed use no compression at all but, rather, surround the breast tissue with rings of light sources and detectors.
While poor spatial resolution of OM methods remains a challenge, the method does show promise for use in pre-surgical chemotherapy. As Edoardo Ferocino, Politecnico di Milano, Italy, co-author of the work explains, “This technique is able to provide information on the outcome of chemotherapy just weeks after beginning treatment, or possibly even sooner.” Ferocino's group is planning clinical studies to explore the use of OM to monitor and predict the outcome of chemotherapy.
The investigators in Milan are working with a larger consortium on a project known as SOLUS, “Smart Optical and Ultrasound Diagnostics of Breast Cancer.” This project is funded by the European Union through the Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program and aims to combine optical imaging methods with ultrasound to improve specificity in the diagnosis of breast cancer.
###
Registration Information
Credentialed media and analysts who wish to cover OSA Biophotonics Congress are welcome to submit a form to register for a full-access conference media badge. Send registration requests to: MediaRelations@osa.org.
About The Optical Society
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional organization for scientists, engineers, students and business leaders who fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership initiatives, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of optics and photonics experts. For more information, visit osa.org.
Media Contacts:
Rebecca B. Andersen
The Optical Society
randersen@osa.org
1-202-416-1443
Joshua Miller
The Optical Society
jmiller@osa.org
1-202-416-1435
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…