3-D printed kidney phantoms aid nuclear medicine dosing calibration

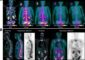
This is a photograph of smallest to largest: newborn, 1-y-old, 5-y-old, and adult. Credit: University of Würzburg
In a study reported in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, researchers at the University of Würzburg in Würzburg, Germany, demonstrated that low-cost 3D printing technology can be used for clinical prototyping. Johannes Tran-Gia, PhD, the study's corresponding author, explains:
“This research shows a way of producing inexpensive models of patient-specific organs/lesions for providing direct and patient-specific calibration constants. This is particularly important for imaging systems suffering from poor spatial resolution and ill-defined quantification, such as SPECT/CT.”
To demonstrate the potential of 3D printing techniques for quantitative SPECT/CT imaging, kidneys–as organs-at-risk in many radionuclide therapies–were selected for the study.
A set of four one-compartment kidney dosimetry phantoms and their spherical counterparts with filling volumes between 8 mL (newborn) and 123 mL (adult) were designed based on the outer kidney dimensions provided by Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD) guidelines. Based on these designs, refillable, waterproof and chemically stable models were manufactured with a fused deposition modeling 3D printer. Nuclide-dependent SPECT/CT calibration factors for technetium-99m (Tc-99m), lutetium-177 (Lu-177), and iodine-131 (I-131) were then determined to assess the accuracy of quantitative imaging for internal renal dosimetry.
Tran-Gia notes, “Although in our study the kidneys were modeled as a relatively simple one-compartment model, the study represents an important step towards a reliable determination of absorbed doses and, therefore, an individualized patient dosimetry of other critical organs in addition to kidneys.”
Ultimately, affordable 3D printing techniques hold the potential for manufacturing individualized anthropomorphic phantoms in many nuclear medicine clinical applications.
###
Authors of the article “Design and Fabrication of Kidney Phantoms for Internal Radiation Dosimetry using 3D Printing Technology” include Johannes Tran-Gia, Susanne Schlögl, and Michael Lassmann, Department of Nuclear Medicine, University of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany.
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center to view the PDF of the study, including images, and more information about molecular imaging and personalized medicine. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Laurie Callahan at (703) 652-6773 or lcallahan@snmmi.org. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.
About the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to raising public awareness about nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, a vital element of today's medical practice that adds an additional dimension to diagnosis, changing the way common and devastating diseases are understood and treated and helping provide patients with the best health care possible.
SNMMI's more than 17,000 members set the standard for molecular imaging and nuclear medicine practice by creating guidelines, sharing information through journals and meetings and leading advocacy on key issues that affect molecular imaging and therapy research and practice. For more information, visit http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Machine learning algorithm reveals long-theorized glass phase in crystal
Scientists have found evidence of an elusive, glassy phase of matter that emerges when a crystal’s perfect internal pattern is disrupted. X-ray technology and machine learning converge to shed light…

Mapping plant functional diversity from space
HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration. An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong…

Inverters with constant full load capability
…enable an increase in the performance of electric drives. Overheating components significantly limit the performance of drivetrains in electric vehicles. Inverters in particular are subject to a high thermal load,…