Unlocking the power of wood

Wood-derived biomass offers a promising source for cellulose-based fuels, but efforts to exploit this energy have been thwarted by the need for methods to deal with a component of the plant cell wall that binds cellulose and interferes with enzymatic processing.
Termites have developed a natural workaround for this problem. Over the course of evolution, the various ‘lower termite’ species have formed an essential partnership with bacteria and protists dwelling within their gut, these derive support from their termite hosts and in turn facilitate the digestion of the insects’ woody diet.
Glycosyl hydrolase family (GHF) enzymes produced by these symbionts are a key component in the cellulose digestion process, enabling efficient cellulose processing without the need for lignin breakdown. “Some of the enzymes that we have found have more than 10-fold higher activity than current industrial enzymes,” says Shigeharu Moriya of the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute in Wako. Since 2001, Moriya and colleagues have been working to characterize these enzymes, and they have now published their analysis of the various GHFs expressed within the gut protist communities of four lower termite species as well as a related wood-eating cockroach1.
These protists are exceptionally challenging to culture and analyze individually, but can be characterized collectively via ‘metagenomic’ techniques that make it possible to assemble massive gene catalogues from a diverse mixture of cell types. This approach revealed a total of 154 clones representing variants of five different GHFs, and the researchers used this sequence data to assemble a phylogenetic tree—essentially a detailed timeline of the evolutionary history of these genes.
GHF5 and 7 were represented in every termite symbiont community investigated, suggesting that their evolution either precedes or coincides with the emergence of termite–protist symbiosis. Interestingly, the data suggest that GHF5 may have been initially acquired by protists from bacteria over the course of one or more ancient gene transfer events. GHF7, on the other hand, appears to have evolved specifically within protists.
The other three enzyme classes—GHF10, 11 and 45—are less broadly conserved, and the author speculate that they provide support for the core GHF5–GHF7 cellulose degradation machinery. “This system is well conserved among various termites, and it may be composed of high-performance enzymes,” says Moriya. His team is now partnering with other RIKEN teams to develop novel techniques for characterizing the metabolic pathways of these protist communities in an effort to identify additional factors that expedite biomass processing.
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the Biosphere Oriented Biology Research Unit, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
Journal information
1. Todaka, N., Inoue, T., Saita, K., Ohkuma, M., Nalepa, C.A., Lenz, M., Kudo, T. & Moriya, S. Phylogenetic analysis of cellulolytic enzyme genes from representative lineages of termites and a related cockroach. PLoS ONE 5, e8636 (2010)
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
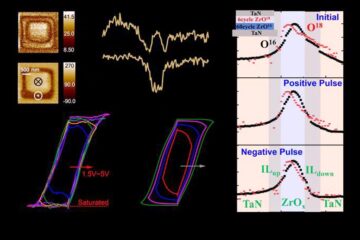
Evidence for reversible oxygen ion movement during electrical pulsing
…enabler of the emerging ferroelectricity in binary oxides. In a recent study published in Materials Futures, researchers have uncovered a pivotal mechanism driving the emergence of ferroelectricity in binary oxides….
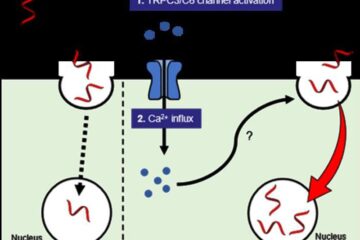
Next-generation treatments hitch a ride into cancer cells
Researchers from Osaka University discover that opening a channel into cancer cells helps antisense oligonucleotide drugs reach their targets. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are next-generation drugs that can treat disease by…

Boron deficiency: oilseed rape reacts as with infection and pest infestation
Genetic mechanisms uncovered… Boron deficiency has a devastating effect on oilseed rape and related plants. However, little is known about the underlying genetic mechanisms. A study shows that the response…





















