Stem-cell-based therapy promising for treatment of breast cancer metastases in the brain
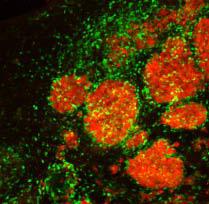
Tagged therapeutic stem cells (green) are targeting breast cancer metastases (red) in the brain of a mouse model. Credit: Khalid Shah, MS, PhD, Massachusetts General Hospital
Investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Harvard Stem Cell Institute have developed an imageable mouse model of brain-metastatic breast cancer and shown the potential of a stem-cell-based therapy to eliminate metastatic cells from the brain and prolong survival.
The study published online in the journal Brain also describes a strategy of preventing the potential negative consequences of stem cell therapy.
“Metastatic brain tumors – often from lung, breast or skin cancers – are the most commonly observed tumors within the brain and account for about 30 percent of advanced breast cancer metastases,” says Khalid Shah, MS, PhD, director of the Molecular Neurotherapy and Imaging Laboratory in the MGH Departments of Radiology and Neurology, who led the study.
“Our results are the first to provide insight into ways of targeting brain metastases with stem-cell-directed molecules that specifically induce the death of tumor cells and then eliminating the therapeutic stem cells.”
In their search for novel, tumor-specific therapies that could target multiple brain metastases without damaging adjacent tissues, the research team first developed a mouse model that more closely mimics what is seen in patients. They found that injecting into the carotid artery breast cancer cells that express markers allowing them to enter the brain – cells labelled with bioluminescent and fluorescent markers to enable tracking by imaging technologies – resulted in the formation of many metastatic tumors throughout the brain, mimicking what is seen in advanced breast cancer patients. Current therapeutic options for such patients are limited, particularly when there are many metastases.
To devise a potential new therapy, the investigators engineered a population of neural stem cells to express a potent version of a gene called TRAIL, which codes for a molecule that activates cell-death-inducing receptors found only on the surface of cancer cells. Previous research by Shah and his colleagues had shown that two types of stem cells are naturally attracted toward tumors in the brain.
After first verifying in their model that stem cells injected to the brain would travel to multiple metastatic sites and not to tumor-free areas, the team implanted TRAIL-expressing stem cells into the brains of metastasis-bearing mice, which reduced the growth of tumors. Injecting the TRAIL-expressing stem cells into the carotid artery, a likely strategy for clinical application, led to significantly slower tumor growth and increased survival, compared with animals receiving unaltered stem cells or control injections.
The safe use of a stem-cell-based therapy against brain metastasis would require preventing the engineered cells from persisting within the brain, where they could affect normal tissue and possibly give rise to new tumors. To facilitate removal of the therapeutic stem cells from the brain at the conclusion of therapy, the researchers created cells that, in addition to TRAIL, express a viral gene called HSV-TK, which renders them susceptible to the effects of the antiviral drug ganciclovir.
Several tests in cultured cells indicated that ganciclovir would cause the death of HSV-TK-expressing stem cells, and testing in the mouse model confirmed that administration of the drug after successful treatment of brain metastases successfully eliminated therapeutic stem cells that also expressed HSV-TK.
Shah and his team are currently developing similar animal models of brain metastasis from lung cancers and from melanoma. They also are working to improve understanding of the therapeutic efficacy of simultaneously targeting multiple tumor-specific molecules on the surface of metastatic cells within the brain and anticipate that their findings will make a major contribution towards developing novel targeted therapies for metastatic tumors in the brain.
###
In addition to Shah, who is an associate professor at Harvard Medical School and a principal faculty member at Harvard Stem Cell Institute, the authors of the Brain report are co-lead authors Wanlu Du, PhD, and Tugba Bagci-Onder, PhD, along with Jose-Luiz Figueiredo, MD, and Jordi Martinez-Quintanilla, PhD – all of the MGH Molecular Neurotherapy and Imaging Laboratory. The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants CA138922 and NS071197 and a grant from the James McDonald Foundation.
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The MGH conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the United States, with an annual research budget of more than $760 million and major research centers in AIDS, cardiovascular research, cancer, computational and integrative biology, cutaneous biology, human genetics, medical imaging, neurodegenerative disorders, regenerative medicine, reproductive biology, systems biology, transplantation biology and photomedicine.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















