Sleeping Beauty enables efficient gene transfer in haematopoietic stem cells of humans
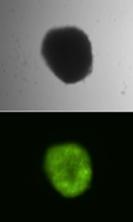
Stable gene transfer and expression of a Venus fluorescence marker gene mediated by Sleeping Beauty transposons in hematopoietic progenitor cells. Source: PEI
In gene therapy of certain congenital disorders, the therapeutic gene is transferred into the target cells using particular transport vehicles, also known as vectors. Gene transfer into haematopoietic (blood forming) stem cells has been successfully tested in clinical trials for the treatment of various genetic disorders caused by a defect in one particular gene (monogenetic).
Examples include certain immune defects such as the group of Severe Combined Immune Deficiency disorders (SCID). In some studies, however, isolated cases of oncogenic mutations triggered by gene vector integration led to cancer (leukaemia) as an undesired side-effect of the therapy. Major efforts have ever since been undertaken to develop safer vector systems.
The research team of Dr Zoltán Ivics, head of Division Medical Biotechnology of the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut uses Sleeping Beauty for therapeutic gene transfer into human cells. The Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon system is a non-viral vector, which is low-cost to manufacture, relatively simple to use. Up to now, its clinical use for hematopoietic stem cell therapy has been hampered by technical challenges.
In an international collaboration with other researchers from Germany, Spain and France, Ivics and his team have shown that gene constructs can be incorporated 20-times more efficiently into the genomes of hematopoietic stem cells if minicircle DNA is used to carry the SB transposon. Minicircle DNA is very small because sequences used for the manufacturing process of plasmids have been removed.
In addition, the efficacy and safety of the stable gene transfer ex vivo (outside the body) into the haematopoietic stem cells could be significantly increased by providing the transposase enzyme in the form of a synthetic messenger DNA (mRNA). This enzyme is required for the gene transfer.
“We have methodologically further developed the Sleeping Beauty transposon system in such a way that clinical use of this method is now possible,” said Dr Ivics, as he described the potential use of these research results.
Background: Transposon “Sleeping Beauty” and jumping genes
A transposon – jumping gene – is a section of DNA which can change its position in the genome (transposition). The ability to integrate itself into the genome can be used for the gene transfer. Sleeping Beauty is an artificial transposon derived from transposons occurring in fish as early as ten million years ago. The name was given to it based on Grimm's fairy tale “Sleeping Beauty”.
Original Publication
Holstein M, Mesa-Nuñez C, Miskey C, Almarza E, Poletti V, Schmeer M, Grueso E, Ordóñez Flores JC, Kobelt D, Walther W, Aneja MK, Geiger J, Bonig HB, Izsvák Z, Schleef M, Rudolph C, Mavilio F, Bueren JA, Guenechea G, Ivics Z (2018):
Efficient Non-viral Gene Delivery into Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells by Minicircle Sleeping Beauty Transposon Vectors.
Mol Ther Jan 17 [Epub ahead of print].
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.01.012
The Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, the Federal Institute for Vaccines and Biomedicines, in Langen near Frankfurt/Main is a senior federal authority reporting to the Federal Ministry of Health (Bundesministerium für Gesundheit, BMG). It is responsible for the research, assessment, and marketing authorisation of biomedicines for human use and immunological veterinary medicinal products. Its remit also includes the authorisation of clinical trials and pharmacovigilance, i.e. recording and evaluation of potential adverse effects.
Other duties of the institute include official batch control, scientific advice and inspections. In-house experimental research in the field of biomedicines and life science form an indispensable basis for the manifold tasks performed at the institute.
The Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, with its roughly 800 members of staff, also has advisory functions nationally (federal government, federal states (Länder)), and internationally (World Health Organisation, European Medicines Agency, European Commission, Council of Europe etc.).
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1525001618300194?via%3Dihub – Open Access full text article
https://www.pei.de/EN/information/journalists-press/press-releases/2018/04-sleep… – Link to this press release on the Website of the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















