Scientists Use X-Ray Vision to Probe Early Stages of DNA 'Photocopying'
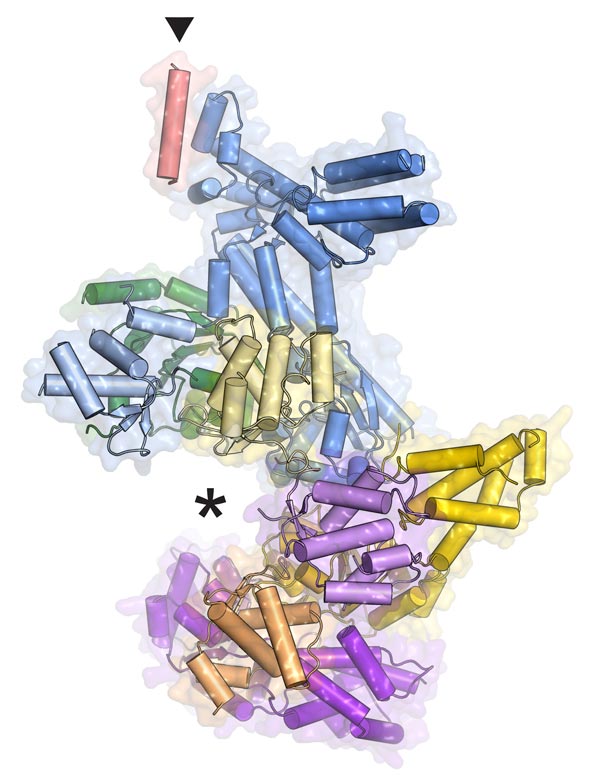
Fraziska Bleichert, James Berger, Johns Hopkins Medicine A simplified model of the ORC protein machine shows where DNA fits (asterisk) and where the Orc6 piece attaches (triangle).
Scientists at Johns Hopkins have created a 3-D model of a complex protein machine, ORC, which helps prepare DNA to be duplicated. Like an image of a criminal suspect, the intricate model of ORC has helped build a “profile” of the activities of this crucial “protein of interest.”
But the new information has uncovered another mystery: ORC’s structure reveals that it is not always “on” as was previously thought, and no one knows how it turns on and off.
A summary of the study will be published in the journal Nature on March 11.
“Even though the ORC protein machinery is crucial to life, we didn’t know much about how it works,” says James Berger, Ph.D., professor of biophysics and biophysical chemistry. “By learning what it looks like, down to the arrangement of each atom, we can get a sense of where it interacts with DNA and how it does its job.”
Multicelled organisms grow when their cells divide into two. However, before a cell can divide, it has to make copies of its parts for the new cell. Since DNA's information is sealed inside its double strands, a specialized machine, called the replisome, must unseal the strands before the information can be accessed and copied.
A key piece of the replisome is a motor, termed MCM, which unwinds paired DNA strands. MCM is a closed protein ring that must be opened up before it can encircle the long strands of DNA. ORC, the origin recognition complex, solves that problem. It cracks open the MCM's circle so that it can fit around the DNA and unwind it.
It was previously known that ORC is a six-piece protein complex, with five of the pieces forming a slightly opened ring and the sixth, Orc6, forming a tail. Mistakes in Orc6 cause assembly problems, which affect the function of the whole machine and contribute to a dwarfism disorder called Meier-Gorlin syndrome.
To learn more about how the complex works, Franziska Bleichert, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in Berger’s laboratory, extracted the protein from fruit fly cells and immobilized it by coaxing it into tiny crystals. She then analyzed its structure by shining high-energy X-rays at the crystals in very focused beams. The resulting data allowed her to reconstruct the precise shape of the proteins, atom by atom, on the scale of billionths of an inch.
Her model reveals exactly where Orc6 connects to the ring of ORC and explains how mistakes in that protein wreak havoc, though why dysfunctional ORC should cause dwarfism is still a mystery.
The 3-D model also showed the existence of an unexpected regulatory mechanism. It was previously thought that ORC was always “on,” just not always present in the nucleus where it does its work. The model shows that it can exist in an inactive state, raising the question: How does it turn on and off?
“In hindsight, it’s not surprising that there is another level of regulation for ORC,” explains Berger. For example, he says, “As soon as an egg cell is fertilized, it has to jump into action to create the embryo through multiple rounds of cell division, which first requires DNA replication. This inactive state might allow egg cells to stockpile ORC inside the nucleus so it’s available when needed.” His team plans to test this idea soon.
Michael Botchan of the University of California, Berkeley, also contributed to the research.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM071747), the National Cancer Institute (CA R37-30490) and the University of California, Berkeley, Miller Institute for Basic Research in Science.
Contact Information
Catherine Kolf
Senior Communications Specialist
ckolf@jhmi.edu
Phone: 443-287-2251
Mobile: 443-440-1929
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.jhmi.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Making diamonds at ambient pressure
Scientists develop novel liquid metal alloy system to synthesize diamond under moderate conditions. Did you know that 99% of synthetic diamonds are currently produced using high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods?[2]…

Eruption of mega-magnetic star lights up nearby galaxy
Thanks to ESA satellites, an international team including UNIGE researchers has detected a giant eruption coming from a magnetar, an extremely magnetic neutron star. While ESA’s satellite INTEGRAL was observing…

Solving the riddle of the sphingolipids in coronary artery disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new…





















