An embryonic stem cell model for Parkinson’s disease
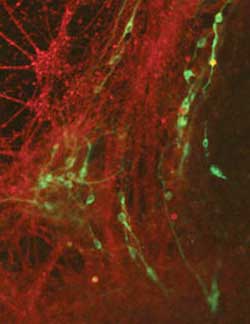
Despite the well-characterized cellular basis of Parkinson’s disease — the degeneration of dopamine-production neurons — the molecular mechanisms responsible for the neurodegeneration remain unknown. Part of the challenge is finding a model that can adequately mimic the loss of dopamine cells. In two papers published in PLoS Biology, Asa Abeliovich and colleagues make the case that a model based on mouse embryonic stem cells offers a promising platform for dissecting the disease mechanism of Parkinson’s.
Working with these cells, the researchers created dopamine neurons deficient in DJ-1, a gene mutated in an inherited form of Parkinson’s. They report that DJ-1-deficient cells — and especially DJ-1-deficient dopamine neurons — display heightened sensitivity to oxidative stress, caused by products of oxygen metabolism that react with and damage cellular components like proteins and DNA. In a second paper, they link DJ-1 dysfunction to the aggregation of alpha-synuclein, a hallmark of Parkinson’s neuropathology.
Oxidative stress has long been associated with neuronal cell death and neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s. Proving a causal relationship between oxidative stress and neurodegeneration, however, requires establishing a molecular mechanism. These results support a link between oxidative damage and disease, and provide a tractable model for both studying the molecular mechanisms of neurodegenerative disease and screening potential neuroprotectant drugs. The authors are hoping to extend their work to human embryonic stem cells, but their work is limited by the availability of such cells under the current NIH guidelines.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.plos.orgAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















