New research project about the genetic modification of cancer cells
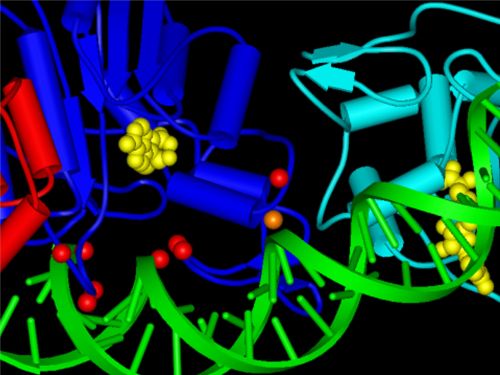
Extract from the structure of the Dnmt3a DNA methyl transferase (red, blue and cyan) with DNA (green). The positions of mutations in tumours are represented by red and orange balls. Illustration: University of Stuttgart
Tumour cells shut down certain genes in the course of the progressing degeneration or mutate these, a process that considerably accelerates the growth of the tumour.
An important role in this process is played by epigenetic factors and thereby in particular DNA methyl transferase (Dnmts), i.e. enzymes that transmit methyl groups on nucleic bases of the DNA. A research group at the Chair for Biochemistry at the University of Stuttgart (Head Prof. Albert Jeltsch) is now investigating in a new project the influence of mutations in the DNA methyl transferase Dnmt3a, that are observed in many leukaemias. The scientists want to elucidate how these modifications contribute towards cancer developing.
The fact that tumour cells shut down or mutate in the course of progressing degeneration has been known for years. Traditionally so-called tumour suppressor genes are affected by this process, that prevent cells with damages in the genome dividing and ultimately drive these cells to a controlled cell death.
However, genes are also frequently damaged or shut down, whose products are involved in the repair of DNA damages. The loss of these factors leads to an increase in mutations in the affected cells, promoting the further progression of tumours.
The rapid development of DNA sequencing technologies has, among other things, led to the identification of many additional mutations in tumour cells. A better understanding of these somatic mutations can help to better understand the process of the tumour developing and to develop targeted therapies for defined sub-types of tumours. A new group of somatically mutated genes are so-called “epigenetic“ factors.
These factors control how strongly genes are transcribed and ultimately through this regulate how the information of the genome is implemented. This group also includes DNA methyl transferase that transmits the methyl groups to the DNA and plays a decisive role in the development of human cells.
It was recently shown that the DNA methyl transferase Dnmt3a is a focal point of somatic tumour mutations in many leukaemias. In this way, up to 30 percent of the patients show a certain mutation in the Dnmt3a gene in a sub-group of leukaemias. This mutation brings about the targeted exchange of an amino acid into another in the protein, comprising a total of 912 amino acids.
Building on its 10 years of experience in investigating Dnmt3a, the workgroup Jeltsch is planning to investigate the effects of these and other tumour mutations in Dnmt3a in the project financed by the German Research Association DFG with the focus on the “Epigenetic Regulation of the normal haematopoiesis and its dysregulation in myeloid neoplasia“.
The results of this project will help to elucidate the tumour-inducing effect of somatic Dnmt3a tumour mutations and to understand how the modifications in the DNA methylation lead to cancer.
Further information:
Prof. Albert Jeltsch, University of Stuttgart, Chair for Biochemistry, 0711/685-64390
Email albert.jeltsch (at) ibc.uni-stuttgart.de
Andrea Mayer-Grenu, University of Stuttgart, Department of University Communication, Tel. 0711/685-82176,
Email: andrea.mayer-grenu (at) hkom.uni-stuttgart.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Solving the riddle of the sphingolipids in coronary artery disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new…

Rocks with the oldest evidence yet of Earth’s magnetic field
The 3.7 billion-year-old rocks may extend the magnetic field’s age by 200 million years. Geologists at MIT and Oxford University have uncovered ancient rocks in Greenland that bear the oldest…

Decisive breakthrough for battery production
Storing and utilising energy with innovative sulphur-based cathodes. HU research team develops foundations for sustainable battery technology Electric vehicles and portable electronic devices such as laptops and mobile phones are…





















