New mode of cellular communication discovered in the brain
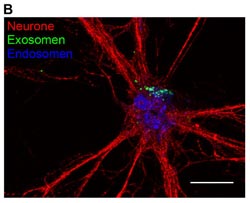
The JGU researchers were able to show that exosomes are absorbed by the nerve cells and thus help protect these against stress.<br> Ill.: Institute of Molecular Cell Biology, JGU<br>
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have discovered a new form of communication between different cell types in the brain. Nerve cells interact with neighboring glial cells, which results in a transfer of protein and genetic information.
Nerve cells are thus protected against stressful growth conditions. The study undertaken by the Mainz-based cell biologists shows how reciprocal communication between the different cell types contributes to neuronal integrity. Their results have been recently published in the journal PLOS Biology.
Brain function is determined by the communication between electrically excitable neurons and the surrounding glial cells, which perform many tasks in the brain. Oligodendrocytes are a type of glial cell and these form an insulating myelin sheath around the axons of neurons. In addition to providing this protective insulation, oligodendrocytes also help sustain neurons in other ways that are not yet fully understood. If this support becomes unavailable, axons can die off. This is what happens in many forms of myelin disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, and it results in a permanent loss of neuron impulse transmission.
Like other types of cell, oligodendrocytes also secrete small vesicles. In addition to lipids and proteins, these membrane-enclosed transport packages also contain ribonucleic acids, in other words, genetic information. In their study, Carsten Frühbeis, Dominik Fröhlich, and Wen Ping Kuo of the Institute of Molecular Cell Biology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz found that oligodendrocytes release nano-vesicles known as 'exosomes' in response to neuronal signals. These exosomes are taken up by the neurons and their cargo can then be used for neuronal metabolism. “This works on a kind of ‘delivery on call’ principle,” explained Dr. Eva-Maria Krämer-Albers, who is leading the current study. “We believe that what are being delivered are 'care packages' that are sent by the oligodendrocytes to neurons.”
While studying cell cultures, the research group discovered that the release of exosomes is triggered by the neurotransmitter glutamate. By means of labeling them with reporter enzymes, the researchers were able to elegantly demonstrate that the small vesicles are absorbed into the interior of the neurons. “The entire package of substances, including the genetic information, is apparently utilized by the neurons,” said Krämer-Albers. If neurons are subjected to stress, cells that have been aided with 'care packages' subsequently recover. “This maintenance contributes to the protection of the neurons and probably also leads to de novo synthesis of proteins,” stated Carsten Frühbeis and Dominik Fröhlich. Among the substances that are present in the exosomes and are channeled to the neurons are, for instance, protective proteins such as heat shock proteins, glycolytic enzymes, and enzymes which counter oxidative stress.
The study has demonstrated that exosomes from oligodendrocytes participate in a previously unknown form of bidirectional cell communication that could play a significant role in the long-term preservation of nerve fibers. “An interaction like this, in which an entire package of substances including genetic information is exchanged between cells of the nervous system, has not previously been observed”, stated Krämer-Albers, summarizing the results. “Exosomes are thus similar to viruses in certain respects, with the major difference that they do not inflict damage on the target cells but are instead beneficial.” In the future, the researchers hope to develop exosomes as possible 'cure' packages that could be used in the treatment of nerve disorders.
Images:
http://www.uni-mainz.de/bilder_presse/10_zellbiologie_exosom_01.jpg
Exosomes (red arrow) are small vesicles that contain proteins and nucleic acids. They are commonly present in close proximity to nerve cell axons where they are ideally positioned to supply protective substances.
Ill.: Institute of Molecular Cell Biology, JGU
http://www.uni-mainz.de/bilder_presse/10_zellbiologie_exosom_02.jpg
The JGU researchers were able to show that exosomes are absorbed by the nerve cells and thus help protect these against stress.
Ill.: Institute of Molecular Cell Biology, JGU
Publication:
Carsten Frühbeis, Dominik Fröhlich, Wen Ping Kuo et al.
Neurotransmitter-Triggered Transfer of Exosomes Mediates Oligodendrocyte-Neuron Communication
PLoS Biology, 9 July 2013
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001604
Further information:
Dr. Eva-Maria Krämer-Albers
Institute of Molecular Cell Biology / Biology for Medical Scientists
Faculty 10: Biology
Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU)
D 55099 Mainz, GERMANY
phone +49 6131 39-26257
fax +49 6131 39-23840
e-mail: alberse@uni-mainz.de
http://www.uni-mainz.de/FB/Biologie/Molekulare-Zellbiologie
Weitere Informationen:
http://www.plosbiology.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.1001604 (Article)
http://www.plosbiology.org (Article in Weekly Editors' Picks)
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-mainz.de/FB/Biologie/Molekulare-ZellbiologieAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















