New Insights into Cell Division – Max Planck Researchers Develop Minimal System
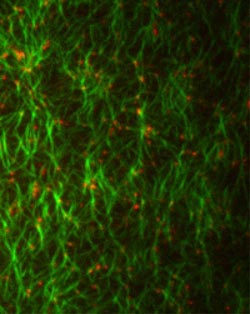
Motor protein (red) bind to actin filaments (green) - a first step to the physical division of a cell.<br><br>Picture: Sven Vogel / Copyright: MPI of Biochemistry<br>
However, it is not yet fully understood just how this important process takes place. Scientists at the MPI of Biochemistry have now developed a minimal biological system, which brings together key components of the cell division apparatus. With the aid of this minimal model, the researchers were able to take a closer look at the biophysical mechanisms involved.
“Our model may help to develop and test new treatments for diseases caused by errors in cell division,” said Sven Vogel, scientist at the MPI of Biochemistry. The results have now been published in the journal eLife.
The researchers of the department “Cellular and Molecular Biophysics” try to remodel the structures of a cell with the help of a modular approach. Their aim is to observe and visualize step by step the underlying mechanisms of living systems. “Our vision is to assemble more and more building blocks of natural and synthetic biomolecules until we finally have the minimal version of a cell in front of us,” said Petra Schwille, director at the MPI of Biochemistry. Using such an approach, the scientists have now succeeded in investigating the process of cell division in greater detail.
Making two out of one
During cell division both the genetic information and the cell plasma must be distributed correctly to the two daughter cells. Moreover, the two newly created cells must be separated physically from each other. An important component of this cell division machinery is the cell cortex. This layer is located directly below the cell membrane and consists of a thin layer of thread-like protein chains, so-called actin filaments. During the actual division process, myosin motors from the interior of the cell exert force on the actin filaments, causing the cell cortex to constrict in the middle and ultimately to divide.
The Max Planck researchers have now constructed an artificial minimal actin cortex (MAC) on which they can study the physical phenomena more precisely. To achieve this, the researchers combined only the most essential components of the cell division machinery, thus creating a synthetic minimal system. Such a system is a very simplified model for complex processes. In nature, by contrast, cells took several million years to develop and were not precisely planned and constructed. “For that reason some of the processes may be more complex than they theoretically need to be,” the biophysicist Sven Vogel said. “This complexity often makes it almost impossible to study the basic mechanisms in detail.”
One research finding the minimal system revealed was that the addition of myosin motors to the MAC induces actin pattern formation. Moreover, the myosin motors break individual actin filaments into fragments and compact them. The Martinsried researchers are certain that artificial minimal systems will contribute to a detailed understanding of cell division. Vogel added: “Our findings and minimal systems may help to develop and test new treatments for diseases that are caused by errors in cell division.”
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















