Innate Lymphoid Cells Elicit T Cell Responses
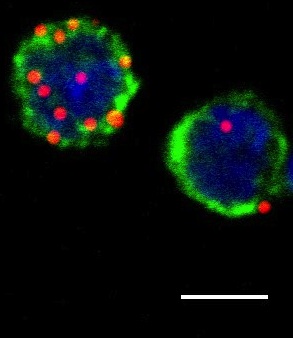
Innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) with internalized antigens (red fluorescent dots). Illustration: University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine
A research group from the Department of Biomedicine at the University and the University Children’s Hospital of Basel now discovered that innate lymphoid cells become activated and induce specific T and B cell responses during inflammation.
These lymphoid cells are thus an important target for the treatment of infection and chronic inflammation. The study was recently published in the scientific journal PNAS.
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are immune cells that regulate early immune responses against viruses, bacteria and parasites through the release of soluble factors. These cells can be classified into three subsets that each have various functions. Type 3 ILCs (ILC3s) are in addition essential for the development of lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes and for tissue repair.
ILC3s internalize antigen and induce T cell responses
The research group lead by Prof. Daniela Finke found that ILC3s take up antigens and present these via so-called MHC molecules on their surface. Specific T cells then recognize these antigen-loaded MHC molecules and induce immune responses. The importance of this interaction between ILC3s and T cells for the immune defense was shown in mice that were lacking the MHC molecules on their ILC3s. These animals had severely reduced T and B cell immune responses.
Inflammatory signals activate ILC3s
So far, scientists assumed that ILC3s decreased T cell responses because they were lacking certain additional receptors required for efficient T cell stimulation. The research group of Prof. Finke was able to show for the first time that these important costimulatory receptors are produced by ILC3s when they are activated through inflammatory signals such as the soluble factor IL-1β. Moreover, ILC3s then produce factors that promote T cell responses.
The results of the Basel research team open up new ways for improving immune responses after vaccination and for preventing harmful immune responses for example during chronic inflammation.
Original source
Nicole von Burg, Stéphane Chappaz, Anne Baerenwaldt, Edit Horvath, Somdeb Bose Dasgupta, Devika Ashok, Jean Pieters, Fabienne Tacchini-Cottier, Antonius Rolink, Hans Acha-Orbea, and Daniela Finke
Activated group 3 innate lymphoid cells promote T-cell-mediated immune responses
PNAS; published online 18 August 2014 | doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406908111
Further information
Prof. Dr. Daniela Finke, University of Basel, Department Biomedicine, and University Children’s Hospital Basel, phone: +41 61 695 30 71, email: daniela.finke@unibas.ch
http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2014/08/15/1406908111.abstract – Abstract
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















