Highly Reactive Gold Carbene Complex Shines in Emerald Green
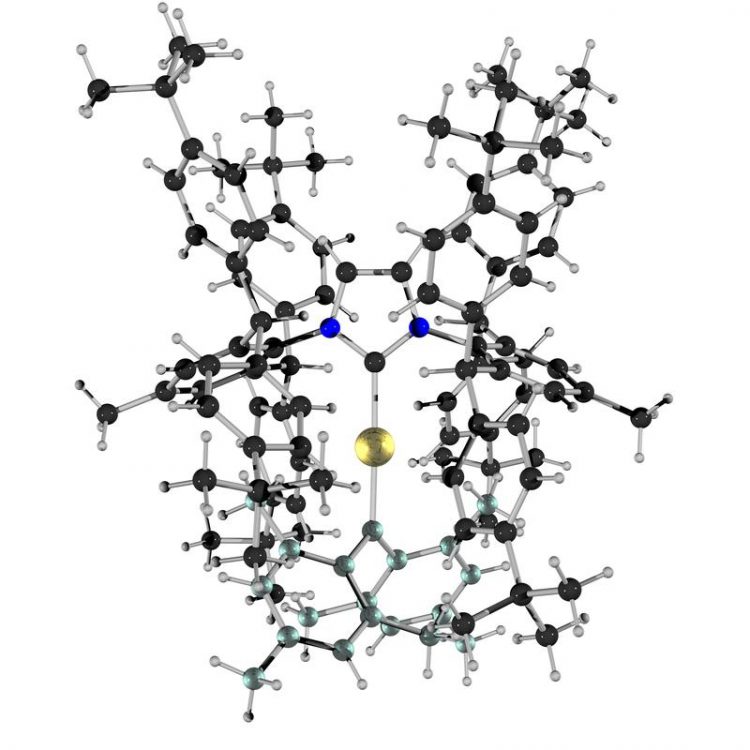
The Au=C double bond in the gold carbene compound is the bond between the large golden atom in the middle and the slightly greenish atom below. The position of the atoms was derived from an x-ray crystal structure analysis. Copyright: Matthias Hussong and Bernd F. Straub, Heidelberg University
With a chemical “trick”, scientists at Heidelberg University have succeeded in isolating a stable gold carbene complex. Chemist Prof. Dr. Bernd F. Straub and his team are the first to have created the basis for directly examining the otherwise unstable gold-carbon double bond. Prof. Straub explains that highly reactive gold carbene molecules play an important role in landmark catalysing processes taking place at high speed. The research findings have been published in the German and the international edition of „Angewandte Chemie“, a journal on applied and fundamental chemistry.
Chemical reactions can be accelerated with the aid of catalysts; consequently materials and pharmaceuticals can be manufactured from the raw materials of nature. The study of gold compounds in catalytic processes has proved particularly intensive and successful, according to Prof. Straub. “In numerous scientific studies in the last ten years, experts have been proposing gold carbenes as essential short-lived intermediates in catalytic reactions,” the Heidelberg researcher explains. However, with their high reactivity they escape detailed study: hardly has a gold carbene fragment consisting of the elements gold and carbon emerged – Au for aurum and C for carbon – when it continues to react.
In order to first create a stable complex and isolate a gold carbene structure for research, the two elements were “lured into a cage like a hungry tiger with a bait,” says Matthias Hussong, who is working on his doctoral dissertation in Prof. Straub’s team. The researchers first shielded the gold and carbon from its environment by surrounding them with low-reactive, space-filling chemical groups. Then the two elements were bonded in a carefully planned step – and so the Au=C fragment was “caught” in the gold carbene complex.
The chemists were able to impart “an amazing stability” to the gold carbene, says Prof. Straub – and at the same time to make it literally visible. “Almost all gold complexes are colourless, while the ‘stable’ gold carbene is emerald green,” states the scientist, who heads a research group at Heidelberg University‘s Institute of Organic Chemistry. Further Heidelberg studies showed that gold in its compounds is more than a “soft proton”, as the chemical behaviour of gold had been described to date.
If the gold fragment is replaced by a “real” proton, e.g. the nucleus of hydrogen, the lightest element, this analogous protonated carbene displays a reddish purple colour. “The gold in the gold carbene complex behaves differently from a proton – that is very clear to the eye,” states Prof. Straub. He and his team are now continuing to explore the understanding of gold catalysis, with the aim of using these findings to make catalytic processes more efficient.
Original publications:
Hussong, M. W., Rominger, F., Krämer, P. und Straub, B. F.: Isolierung eines nicht-Heteroatom-stabilisierten Goldcarbens. Angew. Chem. (online veröffentlicht am 20. Juni 2014), doi: 10.1002/ange.201404032
Hussong, M. W., Rominger, F., Krämer, P. and Straub, B. F.: Isolation of a Non-Heteroatom-Stabilized Gold–Carbene Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (published online 20 June 2014), doi: 10.1002/anie.201404032
Internet information:
http://www.uni-heidelberg.de/fakultaeten/chemgeo/oci/akstraub/index.html
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Bernd F. Straub
Institute of Organic Chemistry
Phone: +49 6221 54-6239
straub@oci.uni-heidelberg.de
Communications and Marketing
Press Office, phone: +49 6221 54-2311
presse@rektorat.uni-heidelberg.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
In a significant milestone for quantum communication technology, an experiment has demonstrated how networks can be leveraged to combat disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communications. The international effort led by researchers…

Stretchable quantum dot display
Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes achieved record-breaking performance. A team of South Korean scientists led by Professor KIM Dae-Hyeong of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for…

Internet can achieve quantum speed with light saved as sound
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute have developed a new way to create quantum memory: A small drum can store data sent with light in its sonic…





















