Core mechanism for root growth identified
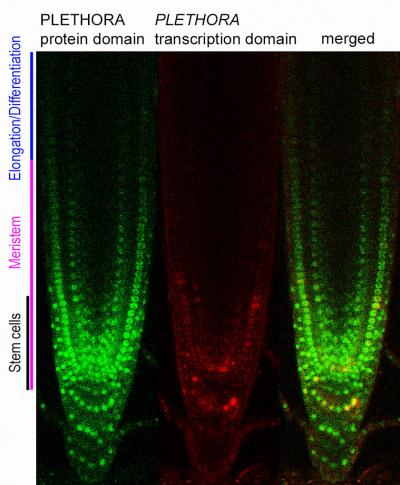
Cell division in the root meristem is maintained by PLETHORA transcription factors solely transcribed in the stem cells. Outside the stem cells the amount of PLETHORA protein in the cells halves each time the cells divide. In the end there is so little PLETHORA left in the cells that they cannot stay in the dividing mode and start to elongate and differentiate. Credit: Ari Pekka Mähönen group, Institute of Biotechnology
Three distinct developmental zones are generated: the meristem, where the cell division takes place, and elongation and differentiation zones. At the same time, plants can rapidly adjust their direction of growth to adapt to environmental conditions.
In Arabidopsis roots, many aspects of zonation are controlled by the plant hormone auxin and auxin-induced PLETHORA transcription factors. Both show a graded distribution with a maximum near the root tip. In addition, auxin is also pivotal for tropic responses of the roots.
Ari Pekka Mähönen with his group in the Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, Finland, and Dutch colleagues has now found out with the help of experimentation and mathematical modelling how the two factors together regulate root growth.
“Cell division in the meristem is maintained by PLETHORA transcription factors. These proteins are solely transcribed in the stem cells, in a narrow region within the meristematic cells located in the tip of the root. So PLETHORA proteins are most abundant in the stem cells,” Ari Pekka Mähönen says.
Outside the stem cells the amount of PLETHORA protein in the cells halves each time the cells divide. In the end there is so little PLETHORA left in the cells that they cannot stay in the dividing mode. This is when the cells start to elongate and differentiate.
Auxin is the factor taking care of many aspects of root growth. If there is enough PLETHORA in the root cells, auxin affects the rate of root cell division. If there is little or no PLETHORA in the cells, auxin regulates cell differentiation and elongation. In addition to this direct, rapid regulation, auxin also regulates cell division, expansion and differentiation indirectly and slowly by promoting PLETHORA transcription. This dual action of auxin keeps the structure and growth of the root very stable.
When PLETHORA levels gradually diminish starting from the root tip upwards, the cell division, elongation and differentiation zones are created. And this inner organisation stays even if the growth direction of the root changes.
“The gravity and other environmental factors can change the auxin content of the cells, and quite rapidly. This all affects the growth direction of the root. And of course it is important for the plant to maintain the organization while directing their roots there where water and nutrients most likely are to be found.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.helsinki.fiAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















