Complete skin regeneration system of fish unraveled
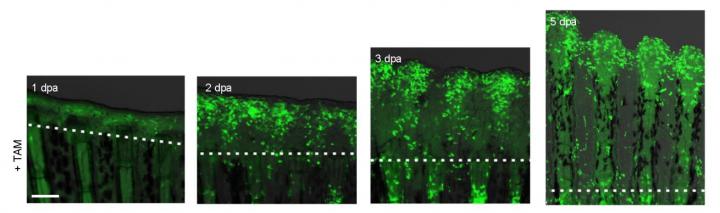
Cre-loxP was used as the cell-labeling technique. In this case, EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein) expression in the regenerative epidermis of zebrafish fins was switched on by using recombination enzyme Cre expressed under the regulation of the gene fibronectin 1b. Recombination can be induced by using a compound called tamoxifen (TAM). *dpa: the number of days since amputation Credit: Tokyo Institute of Technology
The research group led by Tokyo Tech's Associate Professor Atsushi Kawakami, graduate student Eri Shibata, and others used the regeneration of zebrafish fins as a model and labeled the cells of the regenerative tissue with fluorescence (Figure 1) using a genetic cell-labeling technique (Cre-loxP site-specific recombination) and tracked their fates over weeks. As a result, they determined that epithelial cells near a wound follow heterogeneous cell fates.
The first group of epithelial cells which are initially recruited to the wound cover the wound but disappear within a few days by apoptosis. The second group of epithelial cells which arrive later become the cells forming the regenerated skin.
However, many of these regenerated skin cells are moved toward the end of the fin and disappear about one to two weeks. In investigating the source of the replenishing skin cells, it was found that numerous new epithelial cells are supplied in the regeneration process by a large area of skin which contain stem cells and become active in cell proliferation.
Intriguingly, it became clear that skin cells in the regeneration process do not undergo special processes such as de-differentiating into stem cells and regenerating, but existing stem cells in the basal layer and differentiated cells in the surface layer each proliferate with their own characteristics intact to regenerate the skin.
Based on this study, it is conceivable that regeneration of skin would become possible by controlling the autonomous proliferation of stem cells in the basal layer in other vertebrates as well, including humans.
If the mechanism of skin regeneration discovered in this study proves to be the same in humans, it is expected to be used in the future to unravel the causes of various skin diseases, in regenerative medicine research, and for other purposes.
###
Reference
Authors: Eri Shibata, Kazunori Ando, Emiko Murase, and Atsushi Kawakami*
Title of original paper: Heterogeneous fates and dynamic rearrangement of regenerative epidermis-derived cells during zebrafish fin regeneration
Journal: Development
DOI: dev.162016 doi: 10.1242/
Affiliation: School of Life Science and Technology,, Tokyo Institute of Technology
*Corresponding authors email: atkawaka@bio.titech.ac.jp
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















