An unexpected bonus – blocking STAT3 could help cancer patients in two ways
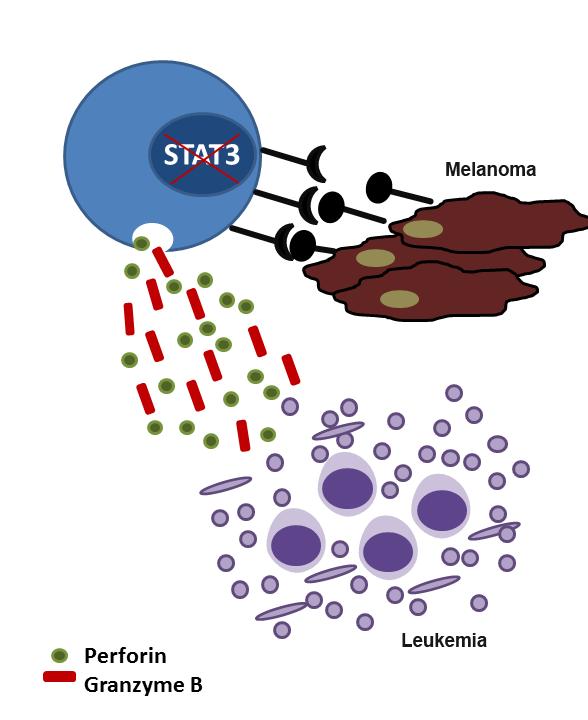
Loss of STAT3 makes NK cells more efficient in recognizing and destroying melanoma cells. Additionally, the excretion of enzymes that fight leukemia cells is increased. (Photo: Dagmar Gotthardt / Vetmeduni Vienna)
However, STAT3 is also important in the development of the immune system. Dagmar Gotthardt and colleagues at the Vetmeduni Vienna now show that blocking STAT3 in cells of the immune system actually leads to increased anti-tumour immunity. Anti-STAT3 therapy may thus be highly promising.
The so-called Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription, or STATs, are key components of many different signalling pathways. Not surprisingly, then, when something goes wrong with their regulation the consequences can be severe and many types of cancer are known to be associated with increased activities of one or more STAT protein.
STAT3 is a frequent culprit and is often found to be activated in tumour cells. Considerable efforts are going into developing inhibitors of STAT3 for use in cancer therapy but it is unclear whether these will turn out to be suitable for use in patients.
The problem is that STAT3 is not all bad but has a number of crucial functions in the healthy body. In particular it is important for the development of several kinds of cells of the immune system. The intriguingly named Natural Killer (NK) cells represent the first line of defence against viruses and cancer, to which they react by producing a range of proteins that attack the infected cells.
It is important to investigate how this key component of the body’s own anti-cancer defence mechanisms might respond to the inactivation of STAT3.
The issue has been tackled by Dagmar Gotthardt and colleagues in the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology of the University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna (Vetmeduni Vienna). Surprisingly, the loss of STAT3 in NK cells of the mouse led not to a decrease but to an increase in killing activity against melanoma cells and leukaemia cells. The decrease in metastasis caused by melanoma cells was especially dramatic and confirmed that NK cells lacking STAT3 are extremely efficient killers of tumour cells.
Gotthardt is naturally excited by the finding. As she says, “we were expecting the loss of STAT3 to make the NK cells less efficient. Instead it makes them even more potent killers. Inhibiting STAT3 could thus help cancer patients in two ways, both stopping the cancer cells from dividing and helping the patients’ NK cells to fight them more efficiently.”
Service:
The article “Loss of STAT3 in murine NK cells enhances NK cell-dependent tumor surveillance”, by Dagmar Gotthardt, Eva M. Putz, Elisabeth Straka, Petra Kudweis, Mario Baggio, Valeria Poli, Birgit Strobl, Mathias Müller and Veronika Sexl was published online on the 9th of October in the journal Blood. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-03-564450
About the University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna
The University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna in Austria is one of the leading academic and research institutions in the field of Veterinary Sciences in Europe. About 1,300 employees and 2,300 students work on the campus in the north of Vienna which also houses five university clinics and various research sites. Outside of Vienna the university operates Teaching and Research Farms. http://www.vetmeduni.ac.at
Scientific Contact:
Prof. Veronika Sexl
Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology
University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna (Vetmeduni Vienna)
T +43 1 25077-2910
veronika.sexl@vetmeduni.ac.at
or
Dagmar Gotthardt
Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology
University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna (Vetmeduni Vienna)
T +43 1 25077-2900
dagmar.gotthardt@vetmeduni.ac.at
Released by:
Susanna Kautschitsch
Science Communication / Public Relations
University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna (Vetmeduni Vienna)
T +43 1 25077-1153
susanna.kautschitsch@vetmeduni.ac.at
http://www.vetmeduni.ac.at/en/infoservice/presseinformation/press-releases-2014/…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















